Rifampin-Associated Flu-Like Syndrome in a Patient Undergoing Treatment for a Device-Related Infection
- PMID: 33520532
- PMCID: PMC7837647
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.12336
Rifampin-Associated Flu-Like Syndrome in a Patient Undergoing Treatment for a Device-Related Infection
Abstract
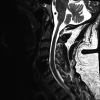
Rifampin (or rifampicin) has found extensive use for the treatment of a variety of infectious illnesses, particularly tuberculosis and device-related infections. We describe the development of a flu-like syndrome in a patient undergoing extended antimicrobial therapy with rifampin for discitis and an associated device-related infection, which promptly resolved with discontinuation of rifampin. While the flu-like syndrome has been documented in prior literature covering the treatment of tuberculosis (where the dose regimen tends to be intermittent) there is less evidence for its occurrence in the treatment of device-related infections (which tend to be dosed daily).
Keywords: device-related infection; rifampicin; rifampin; side-effects.
Copyright © 2020, Calaquian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Osmon DR, Berbari EF, et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;56:0. - PubMed
-
- History of the development of rifampin. Sensi P. Rev Infect Dis. 1983;5:0. - PubMed
-
- Antimicrobial treatment of orthopedic implant-related infections with rifampin combinations. Widmer A, Gaechter A, Ochsner P, Zimmerli W. Clin Infect Dis. 1992;14:1251–1253. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources