An in silico approach to study the interaction of BHA with selected steroid hormone receptors and investigating it's agonistic and antagonistic properties
- PMID: 33520595
- PMCID: PMC7843719
- DOI: 10.1007/s40203-020-00070-x
An in silico approach to study the interaction of BHA with selected steroid hormone receptors and investigating it's agonistic and antagonistic properties
Abstract
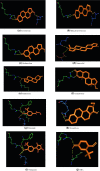
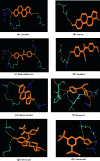
Antioxidant food additives were routinely used for increasing the keeping quality of packaged food items. Butylated Hydroxyanisole (BHA) is one of the most widely used synthetic phenolic antioxidants of such kind. Although quantity of antioxidants in packaged eatables and admissible daily intake (ADI) per person per day are limited by laws, the urbanisation and changes in lifestyle has cross these limits. Although studies on BHA has been carried out, there exists a great deal of uncertainty about the exact molecular mechanism of interaction of BHA with various receptors in the body. Since earlier reports suggested BHA plausibly interferes with reproductive system development, we opted docking of critical receptors of endogenous hormones controlling growth and development of reproductive system with BHA. Nuclear receptors of estrogen (ER), androgen (AR) and progesterone (PR) were selected for this purpose. This manuscript describes the comparison of binding pattern of BHA towards AR, ER and PR along with their agonists and antagonist. Lamarckian Genetic Algorithm of AutoDock 4.0 was used for analysing the mode of binding of ligands with the receptors. It is evident form the docking studies that, BHA exhibited similar binding pattern` with antagonists of AR and agonists of ER. But the interaction of BHA with PR was not compatible with either agonists or antagonists. The docking patterns produced could reliably demonstrate the interactions of BHA with selected receptors and also predict its possible agonistic and antagonistic action.
Keywords: Agonists; Antagonists; Antioxidant; BHA; Molecular docking.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH, DE part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Estimated daily intakes of butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) and tert-butyl hydroquinone (TBHQ) antioxidants in Korea.Food Addit Contam. 2005 Dec;22(12):1176-88. doi: 10.1080/02652030500195288. Food Addit Contam. 2005. PMID: 16356880
-
Estimates of the theoretical maximum daily intake of phenolic antioxidants BHA, BHT and TBHQ in Brazil.Food Addit Contam. 2001 May;18(5):365-73. doi: 10.1080/02652030120645. Food Addit Contam. 2001. PMID: 11358178
-
Antioxidant properties of eugenol, butylated hydroxylanisole, and butylated hydroxyl toluene with key biomolecules relevant to Alzheimer's diseases-In vitro.J Food Biochem. 2021 Mar;45(3):e13276. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13276. Epub 2020 May 26. J Food Biochem. 2021. PMID: 32458455
-
Endocrine disrupting effects of butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA - E320).Clujul Med. 2013;86(1):16-20. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Clujul Med. 2013. PMID: 26527908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic phenolic antioxidants: Metabolism, hazards and mechanism of action.Food Chem. 2021 Aug 15;353:129488. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129488. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 33714793 Review.
References
-
- Carocho M, Morales P, Ferreira ICFR. Trends in food science and technology antioxidants : reviewing the chemistry, food applications, legislation and role as preservatives’, trends in food science and technology. Elsevier. 2018;71:107–120. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2017.11.008. - DOI
-
- DeLano WL (2002) The PyMOL molecular graphics system (http://www.pymol.org)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

