MICAL-L2 Is Essential for c-Myc Deubiquitination and Stability in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells
- PMID: 33520979
- PMCID: PMC7841116
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.575903
MICAL-L2 Is Essential for c-Myc Deubiquitination and Stability in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
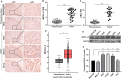
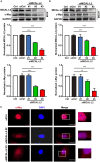
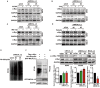
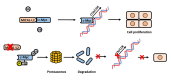
Objectives: MICAL-L2, a member of the molecules interacting with the CasL (MICAL) family, was reported to be highly expressed in several types of cancers, however, the roles of MICAL-L2 in NSCLC pathogenesis remain to be explored. This study is designed to clarify the mechanisms by which MICAL-L2 participates in NSCLC cell proliferation. Materials and Methods: The expression levels of MICAL-L2 in human lung cancer samples were assessed by immunohistochemical staining. Cells were transfected with siRNA or plasmids to regulate MICAL-L2 expression. Cell proliferation was measured by EdU staining and CCK-8 assays. MICAL-L2 and phosphorylated/total c-Myc expression were examined by Western blotting analysis. Interaction between MICAL-L2 and c-Myc was assessed by immunofluorescence staining, Western blotting and co-immunoprecipitation assays. Western blotting, polyubiquitylation detection and protein stability assays were used to assess whether MICAL-L2 exerts its oncogenic effect via c-Myc. Results: We found that MICAL-L2 was highly expressed in human NSCLC. While overexpressing MICAL-L2 increased NSCLC cell proliferation, MICAL-L2 depletion decreased the proliferation of NSCLC cells, an effect that was linked to cell cycle arrest. MICAL-L2 physically interacted with the c-Myc protein and functioned to maintain nuclear c-Myc levels and prolonged its half-life. Knockdown of MICAL-L2 expression led to decreased c-Myc protein stability through accelerating polyubiquitylation of c-Myc and gave rise to c-Myc degradation. We further found that MICAL-L2 deubiquitinated c-Myc and blocked its degradation, presumably by inhibiting c-Myc phosphorylation at threonine residue 58. Conclusions: These results indicate that MICAL-L2 is a key regulator of c-Myc deubiquitination and stability in the nucleus, and this activity may be involved in promoting NSCLC cell proliferation.
Keywords: MICAL-L2; NSCLC; c-Myc; deubiquitination; proliferation.
Copyright © 2021 Min, Zhang, Wang, Qi, Song, Bibi, Zhang, Ma, Zhao, Yu and Du.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

