TET-Mediated Epigenetic Regulation in Immune Cell Development and Disease
- PMID: 33520997
- PMCID: PMC7843795
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.623948
TET-Mediated Epigenetic Regulation in Immune Cell Development and Disease
Abstract
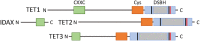
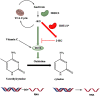
TET proteins oxidize 5-methylcytosine (5mC) to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) and further oxidation products in DNA. The oxidized methylcytosines (oxi-mCs) facilitate DNA demethylation and are also novel epigenetic marks. TET loss-of-function is strongly associated with cancer; TET2 loss-of-function mutations are frequently observed in hematological malignancies that are resistant to conventional therapies. Importantly, TET proteins govern cell fate decisions during development of various cell types by activating a cell-specific gene expression program. In this review, we seek to provide a conceptual framework of the mechanisms that fine tune TET activity. Then, we specifically focus on the multifaceted roles of TET proteins in regulating gene expression in immune cell development, function, and disease.
Keywords: 5hmC; TET proteins; cancer; epigenetics; immune cell development.
Copyright © 2021 Tsiouplis, Bailey, Chiou, Wissink and Tsagaratou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

