The Effect of Different Irrigation Solutions on the Cytotoxicity and Recovery Potential of Human Osteoblast Cells In Vitro
- PMID: 33521208
- PMCID: PMC7819809
- DOI: 10.1016/j.artd.2020.11.004
The Effect of Different Irrigation Solutions on the Cytotoxicity and Recovery Potential of Human Osteoblast Cells In Vitro
Abstract
Background: Surgeons use various irrigation solutions to minimize the risk of prosthetic joint infection after total joint arthroplasty. The toxicity of these solutions is an important consideration in their use. This study investigates the effect of irrigation solutions Bacitracin, Clorpactin (sodium oxychlorosene), and Irrisept (chlorhexidine) on osteoblast cytotoxicity and proliferation.
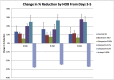
Methods: Four replicates of 6 conditions at 3 time points (1, 2, and 4 min) were tested: control (normal saline), Bacitracin (33 IU/ml), Clorpactin (0.05%, 0.1%, 0.2%), and Irrisept (0.05% chlorhexidine gluconate). Human osteoblasts were cultured at 37°C and 5% CO2 until confluent monolayers were obtained. The treatment solution was applied, and cells were washed 3x with warm phosphate-buffered saline and then supplemented with a fresh medium. Phase-contrast images were taken before and after treatment. The cytotoxicity and proliferation of the treated cells was measured for all conditions on day 3 and day 5 after treatment using the alamarBlue assay.
Results: All test conditions showed morphological changes to cells after treatment; controls did not. Cells demonstrated curling and detachment. This effect was the worst and permanent with Irrisept, whereas other treatments showed a return to normal morphology after 1 week. All treatments showed increased %alamarBlue reduction after 5 days except Irrisept, which showed decreased reduction. There was no statistically significant time or dose dependence with Clorpactin treatment.
Conclusions: Clorpactin and Bacitracin are damaging to human osteoblast cells in vitro as compared with normal saline. This damage is at least partially reversible as shown by morphology and cell viability assay. Irrisept caused more damage than either Clorpactin or Bacitracin, and the damage was not reversible.
Keywords: Basic science; Irrigation solutions; Orthopaedic trauma; Osteoblast toxicity.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of The American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons.
Figures
References
-
- Anglen J.O. Wound irrigation in musculoskeletal injury. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2001;9(4):219. - PubMed
-
- Falagas M.E., Vergidis P.I. Irrigation with antibiotic-containing solutions for the prevention and treatment of infections. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2005;11(11):862. - PubMed
-
- Anglen J.O., Apostoles S., Christensen G., Gainor B. The efficacy of various irrigation solutions in removing slime-producing Staphylococcus. J Orthop Trauma. 1994;8(5):390. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical