A simple ATAC-seq protocol for population epigenetics
- PMID: 33521328
- PMCID: PMC7814285
- DOI: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.15552.2
A simple ATAC-seq protocol for population epigenetics
Abstract
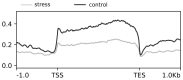
We describe here a protocol for the generation of sequence-ready libraries for population epigenomics studies, and the analysis of alignment results. We show that the protocol can be used to monitor chromatin structure changes in populations when exposed to environmental cues. The protocol is a streamlined version of the Assay for transposase accessible chromatin with high-throughput sequencing (ATAC-seq) that provides a positive display of accessible, presumably euchromatic regions. The protocol is straightforward and can be used with small individuals such as daphnia and schistosome worms, and probably many other biological samples of comparable size (~10,000 cells), and it requires little molecular biology handling expertise.
Keywords: ATAC-seq; Daphnia pulex; Schistosoma mansoni; epigenetics; epigenomics.
Copyright: © 2021 Augusto RdC et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures







References
-
- Boersma M, De Meester L, Spaak P: Environmental stress and local adaptation in Daphnia magna. Limnol Oceanogr. 1999;44(2):393–402. 10.4319/lo.1999.44.2.0393 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

