Dynamic model of COVID-19 disease with exploratory data analysis
- PMID: 33521409
- PMCID: PMC7837064
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00477
Dynamic model of COVID-19 disease with exploratory data analysis
Abstract
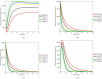
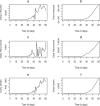
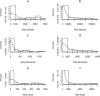
Novel Coronavirus is a highly infectious disease, with over one million confirmed cases and thousands of deaths recorded. The disease has become pandemic, affecting almost all nations of the world, and has caused enormous economic, social and psychological burden on countries. Hygiene and educational campaign programmes have been identified to be potent public health interventions that can curtail the spread of the highly infectious disease. In order to verify this claim quantitatively, we propose and analyze a non-linear mathematical model to investigate the effect of healthy sanitation and awareness on the transmission dynamics of Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) prevalence. Rigorous stability analysis of the model equilibrium points was performed to ascertain the basic reproduction number R 0, a threshold that determines whether or not a disease dies out of the population. Our model assumes that education on the disease transmission and prevention induce behavioral changes in individuals to imbibe good hygiene, thereby reducing the basic reproduction number and disease burden. Numerical simulations are carried out using real life data to support the analytic results.
Keywords: Education; Exploratory data analysis; Hygiene; Reproduction number; Stability.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have agreed and approved the manuscript and have contributed significantly towards the article. There is no conflict of interest among the authors.
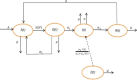
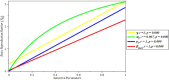
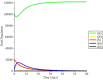
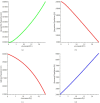
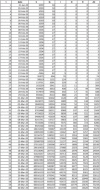
Figures

References
-
- Al-Rousan N., Al-Najjar H. The correlation between the spread of covid-19 infections and weather variables in 30 chinese provinces and the impact of chinese government mitigation plans. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020;24(8) - PubMed
-
- Adhikari S.P., Meng S., Wu Y.-J., Mao Y.-P., Ye R.-X., Wang Q.-Z., Sun C., Sylvia S., Rozelle S., Raat H., et al. Epidemiology, causes, clinical manifestation and diagnosis, prevention and control of coronavirus disease (covid-19) during the early outbreak period: a scoping review. Infect. Dis. Pover. 2020;9(1):1–12. - PMC - PubMed
-
- for Disease Control C., Prevention, et al. Novel coronavirus, Wuhan, China. Prevention. 2020
-
- Novel C.P.E.R.E., et al. The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (covid-19) in china. Zhonghua liu xing bing xue za zhi= Zhonghua liuxingbingxue zazhi. 2020;41(2):145. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
