Clinical and vital sign changes associated with late-onset sepsis in very low birth weight infants at 3 NICUs
- PMID: 33523025
- PMCID: PMC8316489
- DOI: 10.3233/NPM-200578
Clinical and vital sign changes associated with late-onset sepsis in very low birth weight infants at 3 NICUs
Abstract
Background: In premature infants, clinical changes frequently occur due to sepsis or non-infectious conditions, and distinguishing between these is challenging. Baseline risk factors, vital signs, and clinical signs guide decisions to culture and start antibiotics. We sought to compare heart rate (HR) and oxygenation (SpO2) patterns as well as baseline variables and clinical signs prompting sepsis work-ups ultimately determined to be late-onset sepsis (LOS) and sepsis ruled out (SRO).
Methods: At three NICUs, we reviewed records of very low birth weight (VLBW) infants around their first sepsis work-up diagnosed as LOS or SRO. Clinical signs prompting the evaluation were determined from clinician documentation. HR-SpO2 data, when available, were analyzed for mean, standard deviation, skewness, kurtosis, and cross-correlation. We used LASSO and logistic regression to assess variable importance and associations with LOS compared to SRO.
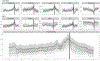
Results: We analyzed sepsis work-ups in 408 infants (173 LOS, 235 SRO). Compared to infants with SRO, those with LOS were of lower GA and BW, and more likely to have a central catheter and mechanical ventilation. Clinical signs cited more often in LOS included hypotension, acidosis, abdominal distension, lethargy, oliguria, and abnormal CBC or CRP(p < 0.05). HR-SpO2 data were available in 266 events. Cross-correlation HR-SpO2 before the event was associated with LOS after adjusting for GA, BW, and postnatal age. A model combining baseline, clinical and HR-SpO2 variables had AUC 0.821.
Conclusion: In VLBW infants at 3-NICUs, we describe the baseline, clinical, and HR-SpO2 variables associated with LOS versus SRO.
Keywords: Neonatal sepsis; bacteremia; infection; predictive modeling; prematurity; vital sign analytics.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
D.E. Lake and J.R. Moorman own stock in Medical Predictive Sciences Corporation. J. R. Moorman is an officer and owns stock in Advanced Medical Predictive Devices, Diagnostics, and Displays.
Figures
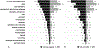
References
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen N. Infections in VLBW infants: Studies from the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Semin Perinatol. 2003;27(4):293–301. - PubMed
-
- Schulman J, Stricof R, Stevens TP, Horgan M, Gase K, Holzman IR, et al. Statewide NICU central-line-associated bloodstream infection rates decline after bundles and check-lists. Pediatrics. 2011;127(3):436–44. - PubMed
-
- Shah J, Jefferies AL, Yoon EW, Lee SK, Shah PS, Canadian Neonatal Network. Risk factors and outcomes of late-onset bacterial sepsis in preterm neonates born at < 32 weeks’ gestation. Am J Perinatol. 2015;32(7):675–82. - PubMed
-
- Shane AL, Stoll BJ. Neonatal sepsis: Progress towards improved outcomes. J Infect. 2014;68(Suppl 1):S24–32. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

