Anwulignan is a novel JAK1 inhibitor that suppresses non-small cell lung cancer growth
- PMID: 33523587
- PMCID: PMC7933975
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16289
Anwulignan is a novel JAK1 inhibitor that suppresses non-small cell lung cancer growth
Abstract
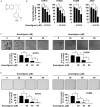
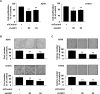
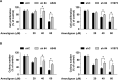
Anwulignan is a monomer compound derived from Schisandra sphenanthera lignans. It has been reported to possess a spectrum of pharmacological activities, including anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, anticancer and hepatoprotective properties. However, its anticancer capacity and molecular mechanism(s) against non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have not been fully elucidated. Anwulignan significantly inhibited cell growth and increased G1-phase cell cycle arrest in NSCLC cells. Anwulignan strongly attenuates the JAK1/STAT3 signalling pathway by directly targeting JAK1 protein kinase activity in vitro. The anticancer activity by Anwulignan is dependent upon the JAK1 protein expression. Remarkably, Anwulignan strongly inhibited tumour growth in vivo. In conclusion, Anwulignan is a novel JAK1 inhibitor that may have therapeutic implications for NSCLC management.
Keywords: Anwulignan; JAK1; NSCLC; STAT3; cell-derived xenograft.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394‐424. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Siegel RL, Jemal A. Lung cancer statistics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;893:1‐19. - PubMed
-
- Lim SM, Syn NL, Cho BC, Soo RA. Acquired resistance to EGFR targeted therapy in non‐small cell lung cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cancer Treat Rev. 2018;65:1‐10. - PubMed
-
- Duruisseaux M, Esteller M. Lung cancer epigenetics: From knowledge to applications. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018;51:116‐128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

