SARS CoV-2 related microvascular damage and symptoms during and after COVID-19: Consequences of capillary transit-time changes, tissue hypoxia and inflammation
- PMID: 33523608
- PMCID: PMC7849453
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.14726
SARS CoV-2 related microvascular damage and symptoms during and after COVID-19: Consequences of capillary transit-time changes, tissue hypoxia and inflammation
Abstract
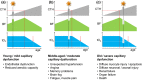
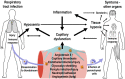
Corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) causes symptoms from multiple organs after infection by severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus 2 (SARS CoV-2). They range from early, low blood oxygen levels (hypoxemia) without breathlessness ("silent hypoxia"), delirium, rashes, and loss of smell (anosmia), to persisting chest pain, muscle weakness and -pain, fatigue, confusion, memory problems and difficulty to concentrate ("brain fog"), mood changes, and unexpected onset of hypertension or diabetes. SARS CoV-2 affects the microcirculation, causing endothelial cell swelling and damage (endotheliitis), microscopic blood clots (microthrombosis), capillary congestion, and damage to pericytes that are integral to capillary integrity and barrier function, tissue repair (angiogenesis), and scar formation. Similar to other instances of critical illness, COVID-19 is also associated with elevated cytokine levels in the systemic circulation. This review examines how capillary damage and inflammation may contribute to these acute and persisting COVID-19 symptoms by interfering with blood and tissue oxygenation and with brain function. Undetectable by current diagnostic methods, capillary flow disturbances limit oxygen diffusion exchange in lungs and tissue and may therefore cause hypoxemia and tissue hypoxia. The review analyzes the combined effects of COVID-19-related capillary damage, pre-existing microvascular changes, and upstream vascular tone on tissue oxygenation in key organs. It identifies a vicious cycle, as infection- and hypoxia-related inflammation cause capillary function to deteriorate, which in turn accelerates hypoxia-related inflammation and tissue damage. Finally, the review addresses the effects of low oxygen and high cytokine levels in brain tissue on neurotransmitter synthesis and mood. Methods to assess capillary functions in human organs and therapeutic means to protect capillary functions and stimulate capillary bed repair may prove important for the individualized management of COVID-19 patients and targeted rehabilitation strategies.
Keywords: COVID-19; brain; capillary dysfunction; heart; hypoxemia; hypoxia; inflammation; long-term symptoms; lungs; microcirculation; muscle.
© 2021 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
LØ is a minority shareholder and Scientific Advisory Board member in Cercare Medical Aps, Denmark and received honoraria for lecturing from Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited.
Figures

References
-
- Ackermann, M. , Verleden, S. E. , Kuehnel, M. , Haverich, A. , Welte, T. , Laenger, F. , Vanstapel, A. , Werlein, C. , Stark, H. , Tzankov, A. , Li, W. W. , Li, V. W. , Mentzer, S. J. , & Jonigk, D. (2020). Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in Covid‐19. New England Journal of Medicine, 383(2), 120–128. 10.1056/NEJMoa2015432 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angleys, H. , & Østergaard, L. (2020). Krogh’s capillary recruitment hypothesis, 100 years on: Is the opening of previously closed capillaries necessary to ensure muscle oxygenation during exercise? American Journal of Physiology‐Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 318(2), H425–H447. 10.1152/ajpheart.00384.2019 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Armulik, A. , Genove, G. , Mae, M. , Nisancioglu, M. H. , Wallgard, E. , Niaudet, C. , He, L. , Norlin, J. , Lindblom, P. , Strittmatter, K. , Johansson, B. R. , & Betsholtz, C. (2010). Pericytes regulate the blood‐brain barrier. Nature, 468(7323), 557–561. 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.07.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

