Adiponectin receptor 1 variants contribute to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy that can be reversed by rapamycin
- PMID: 33523960
- PMCID: PMC7787482
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abb3991
Adiponectin receptor 1 variants contribute to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy that can be reversed by rapamycin
Abstract
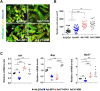
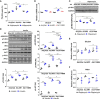
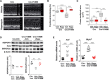
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a heterogeneous genetic heart muscle disease characterized by hypertrophy with preserved or increased ejection fraction in the absence of secondary causes. However, recent studies have demonstrated that a substantial proportion of individuals with HCM also have comorbid diabetes mellitus (~10%). Whether genetic variants may contribute a combined phenotype of HCM and diabetes mellitus is not known. Here, using next-generation sequencing methods, we identified novel and ultrarare variants in adiponectin receptor 1 (ADIPOR1) as risk factors for HCM. Biochemical studies showed that ADIPOR1 variants dysregulate glucose and lipid metabolism and cause cardiac hypertrophy through the p38/mammalian target of rapamycin and/or extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways. A transgenic mouse model expressing an ADIPOR1 variant displayed cardiomyopathy that recapitulated the cellular findings, and these features were rescued by rapamycin. Our results provide the first evidence that ADIPOR1 variants can cause HCM and provide new insights into ADIPOR1 regulation.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures




References
-
- Frey N., Luedde M., Katus H. A., Mechanisms of disease: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 9, 91–100 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Wasserstrum Y., Barriales-Villa R., Fernández-Fernández X., Adler Y., Lotan D., Peled Y., Klempfner R., Kuperstein R., Shlomo N., Sabbag A., Freimark D., Monserrat L., Arad M., The impact of diabetes mellitus on the clinical phenotype of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Eur. Heart J. 40, 1671–1677 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Dhandapany P. S., Sadayappan S., Xue Y., Powell G. T., Rani D. S., Nallari P., Rai T. S., Khullar M., Soares P., Bahl A., Tharkan J. M., Vaideeswar P., Rathinavel A., Narasimhan C., Ayapati D. R., Ayub Q., Mehdi S. Q., Oppenheimer S., Richards M. B., Price A. L., Patterson N., Reich D., Singh L., Tyler-Smith C., Thangaraj K., A common MYBPC3 (cardiac myosin binding protein C) variant associated with cardiomyopathies in South Asia. Nat. Genet. 41, 187–191 (2009). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

