Mass spectrometry imaging identifies abnormally elevated brain l-DOPA levels and extrastriatal monoaminergic dysregulation in l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia
- PMID: 33523980
- PMCID: PMC7787486
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abe5948
Mass spectrometry imaging identifies abnormally elevated brain l-DOPA levels and extrastriatal monoaminergic dysregulation in l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia
Abstract
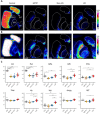
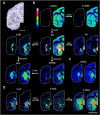
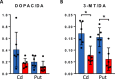
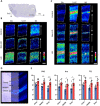
l-DOPA treatment for Parkinson's disease frequently leads to dyskinesias, the pathophysiology of which is poorly understood. We used MALDI-MSI to map the distribution of l-DOPA and monoaminergic pathways in brains of dyskinetic and nondyskinetic primates. We report elevated levels of l-DOPA, and its metabolite 3-O-methyldopa, in all measured brain regions of dyskinetic animals and increases in dopamine and metabolites in all regions analyzed except the striatum. In dyskinesia, dopamine levels correlated well with l-DOPA levels in extrastriatal regions, such as hippocampus, amygdala, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, and cortical areas, but not in the striatum. Our results demonstrate that l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia is linked to a dysregulation of l-DOPA metabolism throughout the brain. The inability of extrastriatal brain areas to regulate the formation of dopamine during l-DOPA treatment introduces the potential of dopamine or even l-DOPA itself to modulate neuronal signaling widely across the brain, resulting in unwanted side effects.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures



References
-
- Ahlskog J. E., Muenter M. D., Frequency of levodopa-related dyskinesias and motor fluctuations as estimated from the cumulative literature. Mov. Disord. 16, 448–458 (2001). - PubMed
-
- de la Fuente-Fernandez R., Sossi V., Huang Z., Furtado S., Lu J.-Q., Calne D. B., Ruth T. J., Stoessl A. J., Levodopa-induced changes in synaptic dopamine levels increase with progression of Parkinson’s disease: Implications for dyskinesias. Brain 127, 2747–2754 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Bastide M. F., Meissner W. G., Picconi B., Fasano S., Fernagut P. O., Feyder M., Francardo V., Alcacer C., Ding Y., Brambilla R., Fisone G., Stoessl A. J., Bourdenx M., Engeln M., Navailles S., De Deurwaerdere P., Ko W. K., Simola N., Morelli M., Groc L., Rodriguez M. C., Gurevich E. V., Quik M., Morari M., Mellone M., Gardoni F., Tronci E., Guehl D., Tison F., Crossman A. R., Kang U. J., Steece-Collier K., Fox S., Carta M., Cenci M. A., Bezard E., Pathophysiology of L-dopa-induced motor and non-motor complications in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 132, 96–168 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Tanaka H., Kannari K., Maeda T., Tomiyama M., Suda T., Matsunaga M., Role of serotonergic neurons in L-DOPA-derived extracellular dopamine in the striatum of 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. Neuroreport 10, 631–634 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

