RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) inhibitors: The current landscape and repurposing for the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 33524687
- PMCID: PMC7826122
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113201
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) inhibitors: The current landscape and repurposing for the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
The widespread nature of several viruses is greatly credited to their rapidly altering RNA genomes that enable the infection to persist despite challenges presented by host cells. Within the RNA genome of infections is RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), which is an essential enzyme that helps in RNA synthesis by catalysing the RNA template-dependent development of phosphodiester bonds. Therefore, RdRp is an important therapeutic target in RNA virus-caused diseases, including SARS-CoV-2. In this review, we describe the promising RdRp inhibitors that have been launched or are currently in clinical studies for the treatment of RNA virus infections. Structurally, nucleoside inhibitors (NIs) bind to the RdRp protein at the enzyme active site, and nonnucleoside inhibitors (NNIs) bind to the RdRp protein at allosteric sites. By reviewing these inhibitors, more precise guidelines for the development of more promising anti-RNA virus drugs should be set, and due to the current health emergency, they will eventually be used for COVID-19 treatment.
Keywords: COVID-19; Nucleoside/non-nucleoside analogue inhibitor; RNA virus; RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp); SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

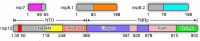


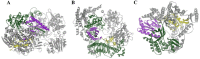


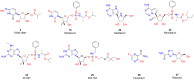
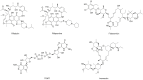

References
-
- Siddharta A., Pfaender S., Vielle N.J., Dijkman R., Friesland M., Becker B., Yang J., Engelmann M., Todt D., Windisch M.P., Brill F.H., Steinmann J., Steinmann J., Becker S., Alves M.P., Pietschmann T., Eickmann M., Thiel V., Steinmann E. Virucidal activity of world health organization-recommended formulations against enveloped viruses, including Zika, ebola, and emerging coronaviruses. JID (J. Infect. Dis.) 2017;215:902–906. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

