COVID-19 convalescent plasma composition and immunological effects in severe patients
- PMID: 33524876
- PMCID: PMC7826092
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102598
COVID-19 convalescent plasma composition and immunological effects in severe patients
Abstract
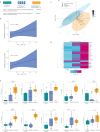
Convalescent plasma (CP) has emerged as a treatment for COVID-19. However, the composition and mechanism of action are not fully known. Therefore, we undertook a two-phase controlled study in which, first the immunological and metabolomic status of recovered and severe patients were evaluated. Secondly, the 28-day effect of CP on the immune response in severe patients was assessed. Nineteen recovered COVID-19 patients, 18 hospitalized patients with severe disease, and 16 pre-pandemic controls were included. Patients with severe disease were treated with CP transfusion and standard therapy (i.e., plasma recipients, n = 9) or standard therapy alone (n = 9). Clinical and biological assessments were done on day 0 and during follow-up on days 4, 7, 14, and 28. Clinical parameters, viral load, total immunoglobulin (Ig) G and IgA anti-S1-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, neutralizing antibodies (NAbs), autoantibodies, cytokines, T and B cells, and metabolomic and lipidomic profiles were examined. Total IgG and IgA anti-S1-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies were key factors for CP selection and correlated with NAbs. In severe COVID-19 patients, mostly interleukin (IL)-6 (P = <0.0001), IL-10 (P = <0.0001), IP-10 (P = <0.0001), fatty acyls and glycerophospholipids were higher than in recovered patients. Latent autoimmunity and anti-IFN-α antibodies were observed in both recovered and severe patients. COVID-19 CP induced an early but transient cytokine profile modification and increases IgG anti-S1-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. At day 28 post-transfusion, a decrease in activated, effector and effector memory CD4+ (P < 0.05) and activated and effector CD8+ (P < 0.01) T cells and naïve B cells (P = 0.001), and an increase in non-classical memory B cells (P=<0.0001) and central memory CD4+ T cells (P = 0.0252) were observed. Moreover, IL-6/IFN-γ (P = 0.0089) and IL-6/IL-10 (P = 0.0180) ratios decreased in plasma recipients compared to those who received standard therapy alone. These results may have therapeutic implications and justify further post-COVID-19 studies.
Keywords: Autoantibodies; COVID-19; Convalescent plasma; Cytokines; Memory cells; Metabolomic profile.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




References
-
- Guan W.-J., Ni Z.-Y., Hu Y., Liang W.-H., Ou C.-Q., He J.-X., Liu L., Shan H., Lei C.-L., Hui D.S.C., Du B., Li L.-J., Zeng G., Yuen K.-Y., Chen R.-C., Tang C.-L., Wang T., Chen P.-Y., Xiang J., Li S.-Y., Wang J.-L., Liang Z.-J., Peng Y.-X., Wei L., Liu Y., Hu Y.-H., Peng P., Wang J.-M., Liu J.-Y., Chen Z., Li G., Zheng Z.-J., Qiu S.-Q., Luo J., Ye C.-J., Zhu S.-Y., Zhong N.-S. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382:1708–1720. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berenguer J., Ryan P., Rodríguez-Baño J., Jarrín I., Carratalà J., Pachón J., Yllescas M., Arriba J.R. vol. 26. The Official Publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases; 2020. pp. 1525–1536. (Characteristics and Predictors of Death Among 4035 Consecutively Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 in Spain., Clinical Microbiology and Infection). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rojas M., Rodríguez Y., Monsalve D.M., Acosta-Ampudia Y., Camacho B., Gallo J.E., Rojas-Villarraga A., Ramírez-Santana C., Díaz-Coronado J.C., Manrique R., Mantilla R.D., Shoenfeld Y., Anaya J.-M. Convalescent plasma in Covid-19: possible mechanisms of action. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020;19:102554. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102554. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Griensven J., Edwards T., de Lamballerie X., Semple M.G., Gallian P., Baize S., Horby P.W., Raoul H., Magassouba N., Antierens A., Lomas C., Faye O., Sall A.A., Fransen K., Buyze J., Ravinetto R., Tiberghien P., Claeys Y., De Crop M., Lynen L., Bah E.I., Smith P.G., Delamou A., De Weggheleire A., Haba N. Evaluation of convalescent plasma for Ebola virus disease in Guinea. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016;374:33–42. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1511812. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

