Extrinsic Regulators of mRNA Translation in Developing Brain: Story of WNTs
- PMID: 33525513
- PMCID: PMC7911671
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10020253
Extrinsic Regulators of mRNA Translation in Developing Brain: Story of WNTs
Abstract
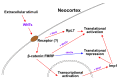
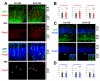
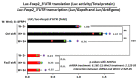
Extrinsic molecules such as morphogens can regulate timed mRNA translation events in developing neurons. In particular, Wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 3 (Wnt3), was shown to regulate the translation of Foxp2 mRNA encoding a Forkhead transcription factor P2 in the neocortex. However, the Wnt receptor that possibly mediates these translation events remains unknown. Here, we report Frizzled member 7 (Fzd7) as the Wnt3 receptor that lays downstream in Wnt3-regulated mRNA translation. Fzd7 proteins co-localize with Wnt3 ligands in developing neocortices. In addition, the Fzd7 proteins overlap in layer-specific neuronal subpopulations expressing different transcription factors, Foxp1 and Foxp2. When Fzd7 was silenced, we found decreased Foxp2 protein expression and increased Foxp1 protein expression, respectively. The Fzd7 silencing also disrupted the migration of neocortical glutamatergic neurons. In contrast, Fzd7 overexpression reversed the pattern of migratory defects and Foxp protein expression that we found in the Fzd7 silencing. We further discovered that Fzd7 is required for Wnt3-induced Foxp2 mRNA translation. Surprisingly, we also determined that the Fzd7 suppression of Foxp1 protein expression is not Wnt3 dependent. In conclusion, it is exhibited that the interaction between Wnt3 and Fzd7 regulates neuronal identity and the Fzd7 receptor functions as a downstream factor in ligand Wnt3 signaling for mRNA translation. In particular, the Wnt3-Fzd7 signaling axis determines the deep layer Foxp2-expressing neurons of developing neocortices. Our findings also suggest that Fzd7 controls the balance of the expression for Foxp transcription factors in developing neocortical neurons. These discoveries are presented in our manuscript within a larger framework of this review on the role of extrinsic factors in regulating mRNA translation.
Keywords: Foxp transcription factor; Fzd7 receptor; ligand Wnt3 signaling; mRNA translation regulation; morphogen factor; neocortical development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Thalamic WNT3 Secretion Spatiotemporally Regulates the Neocortical Ribosome Signature and mRNA Translation to Specify Neocortical Cell Subtypes.J Neurosci. 2015 Aug 5;35(31):10911-26. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0601-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26245956 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interaction between Wnt3 and Frizzled-7 leads to activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.J Hepatol. 2008 May;48(5):780-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.12.020. Epub 2008 Feb 7. J Hepatol. 2008. PMID: 18313787 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA binding protein HuR determines the differential translation of autism-associated FoxP subfamily members in the developing neocortex.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 7;6:28998. doi: 10.1038/srep28998. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27383233 Free PMC article.
-
FOXP transcription factors in vertebrate brain development, function, and disorders.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2020 Sep;9(5):e375. doi: 10.1002/wdev.375. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 31999079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking the Wnt pathway: Therapeutic potential of selective targeting FZD7 in cancer.Drug Discov Today. 2022 Mar;27(3):777-792. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2021.12.008. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Drug Discov Today. 2022. PMID: 34915171 Review.
Cited by
-
Translational control in cortical development.Front Neuroanat. 2023 Jan 9;16:1087949. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2022.1087949. eCollection 2022. Front Neuroanat. 2023. PMID: 36699134 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of the Neocortex Through RNA-Binding Proteins and Post-transcriptional Regulation.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jan 10;15:803107. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.803107. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35082597 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

