Breast Milk for Term and Preterm Infants-Own Mother's Milk or Donor Milk?
- PMID: 33525560
- PMCID: PMC7912320
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13020424
Breast Milk for Term and Preterm Infants-Own Mother's Milk or Donor Milk?
Abstract
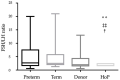
Hormones are important biological regulators, controlling development and physiological processes throughout life. We investigated pituitary hormones such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), prolactin (PRL) and total protein levels during the first 6 months of lactation. Breast milk samples were collected every fourth week of lactation from mothers who gave birth to preterm (n = 14) or term (n = 16) infants. Donor milk is suggested when own mother's milk is not available; therefore, we collected breast milk samples before and after Holder pasteurization (HoP) from the Breast Milk Collection Center of Pécs, Hungary. Three infant formulas prepared in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit of the University of Pécs were tested at three different time points. Our aim was to examine the hormone content of own mother's milk and donor milk. There were no significant changes over time in the concentrations of any hormone. Preterm milk had higher PRL (28.2 ± 2.5 vs 19.3 ± 2.3 ng/mL) and LH (36.3 ± 8.8 vs 15.9 ± 4.1 mIU/L) concentrations than term milk during the first 6 months of lactation. Total protein and FSH concentrations did not differ between preterm and term breast milk. Holder pasteurization decreased the PRL concentration (30.4 ± 1.8 vs 14.4 ± 0.6 ng/mL) and did not affect gonadotropin levels of donor milk. Infant formulas have higher total protein content than breast milk but do not contain detectable levels of pituitary hormones. Differences were detected in the content of pituitary hormones produced for preterm and term infants. Divergence between feeding options offers opportunities for improvement of nutritional guidelines for both hospital and home feeding practices.
Keywords: FSH; LH; PRL; breast milk; infant formula; nutrition; pituitary hormones; preterm newborns.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical