The Interactions between Polyphenols and Microorganisms, Especially Gut Microbiota
- PMID: 33525629
- PMCID: PMC7911950
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10020188
The Interactions between Polyphenols and Microorganisms, Especially Gut Microbiota
Abstract
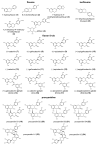
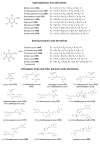
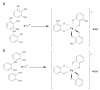
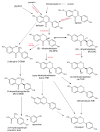
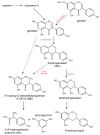
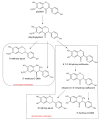
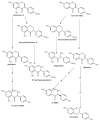
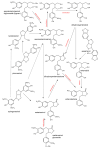
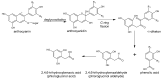
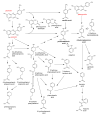
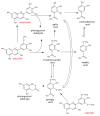
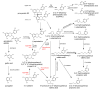
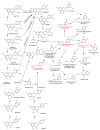
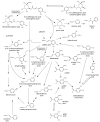
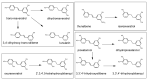
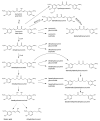
This review presents the comprehensive knowledge about the bidirectional relationship between polyphenols and the gut microbiome. The first part is related to polyphenols' impacts on various microorganisms, especially bacteria, and their influence on intestinal pathogens. The research data on the mechanisms of polyphenol action were collected together and organized. The impact of various polyphenols groups on intestinal bacteria both on the whole "microbiota" and on particular species, including probiotics, are presented. Moreover, the impact of polyphenols present in food (bound to the matrix) was compared with the purified polyphenols (such as in dietary supplements) as well as polyphenols in the form of derivatives (such as glycosides) with those in the form of aglycones. The second part of the paper discusses in detail the mechanisms (pathways) and the role of bacterial biotransformation of the most important groups of polyphenols, including the production of bioactive metabolites with a significant impact on the human organism (both positive and negative).
Keywords: bioactive compounds; biotransformation; catabolism; diversity; health; inhibition; intestinal microbiota; metabolism; metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








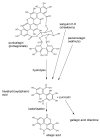
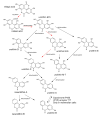
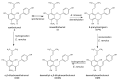
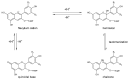
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

