Veno-Venous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in COVID-19-Where Are We Now?
- PMID: 33525739
- PMCID: PMC7908448
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18031173
Veno-Venous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in COVID-19-Where Are We Now?
Abstract
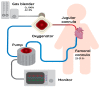
The recent development in extracorporeal life support (ECLS) has created new therapeutic opportunities for critically ill patients. An interest in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), the pinnacle of ECLS techniques, has recently increased, as for the last decade, we have observed improvements in the survival of patients suffering from severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) while on ECMO. Although there is a paucity of conclusive data from clinical research regarding extracorporeal oxygenation in COVID-19 patients, the pathophysiology of the disease makes veno-venous ECMO a promising option.
Keywords: acute respiratory distress syndrome; acute respiratory failure; coronavirus disease 2019; veno-venous extracorporeal oxygenation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Peek G.J., Clemens F., Elbourne D., Firmin R., Hardy P., Hibbert C., Killer H., Mugford M., Thalanany M., Tiruvoipati R., et al. CESAR: Conventional ventilatory support vs extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe adult respiratory failure. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2006;6:163. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-6-163. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alshahrani M.S., Sindi A., Alshamsi F., Al-Omari A., El Tahan M., Alahmadi B., Zein A., Khatani N., Al-Hameed F., Alamri S., et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Ann. Intensive Care. 2018;8:3. doi: 10.1186/s13613-017-0350-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

