The therapeutic potential of bacteriocins as protein antibiotics
- PMID: 33525816
- PMCID: PMC7243282
- DOI: 10.1042/ETLS20160016
The therapeutic potential of bacteriocins as protein antibiotics
Abstract
The growing incidence of antibiotic-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections poses a serious threat to public health. Molecules that have yet to be exploited as antibiotics are potent protein toxins called bacteriocins that are produced by Gram-negative bacteria during competition for ecological niches. This review discusses the state of the art regarding the use for therapeutic purposes of two types of Gram-negative bacteriocins: colicin-like bacteriocins (CLBs) and tailocins. In addition to in vitro data, the potency of eight identified CLBs or tailocins has been demonstrated in diverse animal models of infection with no adverse effects for the host. Although the characteristics of bacteriocins will need further study, results obtained thus far regarding their in vivo potency, immunogenicity and low levels of resistance are encouraging. This leads the way for the development of novel treatments using bacteriocins as protein antibiotics.
Keywords: antibiotics; bacteriocins; colicin; infection; pyocin.
© 2017 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The University of Glasgow has filed patents on the use of the protein antibiotics (colicins and pyocins) as therapeutics with DW listed as an inventor. The University of Oxford has filed a patent on methods for the discovery and engineering of bacteriocins with CK listed as an inventor. The authors have no other conflicts of interest.
Figures
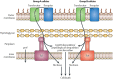

References
-
- Cadman H. and Marinez L. (eds) (2014) Antimicrobial Resistance Global Report on Surveillance, World Health Organization, pp. 1–42
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) (2015) Antimicrobial resistance surveillance in Europe 2014. Annual Report of the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net), ECDC, Stockholm, pp. 1–118
-
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention (2011) Gram-negative bacteria infections in healthcare settings [Internet]. http://www.cdc.gov/hai/organisms/gram-negative-bacteria.html
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
