Macrophage autophagy protects mice from cerium oxide nanoparticle-induced lung fibrosis
- PMID: 33526046
- PMCID: PMC7852145
- DOI: 10.1186/s12989-021-00398-y
Macrophage autophagy protects mice from cerium oxide nanoparticle-induced lung fibrosis
Abstract
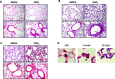
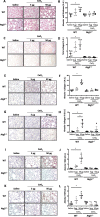
Background: Cerium (Ce) is a rare earth element, rapidly oxidizing to form CeO2, and currently used in numerous commercial applications, especially as nanoparticles (NP). The potential health effects of Ce remain uncertain, but literature indicates the development of rare earth pneumoconiosis accompanied with granuloma formation, interstitial fibrosis and inflammation. The exact underlying mechanisms are not yet completely understood, and we propose that autophagy could be an interesting target to study, particularly in macrophages. Therefore, the objective of our study was to investigate the role of macrophagic autophagy after pulmonary exposure to CeO2 NP in mice. Mice lacking the early autophagy gene Atg5 in their myeloid lineage and their wildtype counterparts were exposed to CeO2 NP by single oropharyngeal administration and sacrificed up to 1 month after. At that time, lung remodeling was thoroughly characterized (inflammatory cells infiltration, expression of fibrotic markers such as αSMA, TGFβ1, total and type I and III collagen deposition), as well as macrophage infiltration (quantification and M1/M2 phenotype).
Results: Such pulmonary exposure to CeO2 NP induces a progressive and dose-dependent lung fibrosis in the bronchiolar and alveolar walls, together with the activation of autophagy. Blockage of macrophagic autophagy protects from alveolar but not bronchiolar fibrosis, via the modulation of macrophage polarization towards M2 phenotype.
Conclusion: In conclusion, our findings bring novel insight on the role of macrophagic autophagy in lung fibrogenesis, and add to the current awareness of pulmonary macrophages as important players in the disease.
Keywords: Alveolar fibrosis - autophagy - macrophage polarization; Nanoparticle.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interest to declare.
Figures





References
-
- Gwenzi W, Mangori L, Danha C, Chaukura N, Dunjana N, Sanganyado E. Sources, behaviour, and environmental and human health risks of high-technology rare earth elements as emerging contaminants. Sci Total Environ. 2018;636:299–313. - PubMed
-
- Cassee FR, van Balen EC, Singh C, Green D, Muijser H, Weinstein J, et al. Exposure, health and ecological effects review of engineered nanoscale cerium and cerium oxide associated with its use as a fuel additive. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2011;41(3):213–229. - PubMed
-
- Porru S, Placidi D, Quarta C, Sabbioni E, Pietra R, Fortaner S. The potencial role of rare earths in the pathogenesis of interstitial lung disease: a case report of movie projectionist as investigated by neutron activation analysis. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2001;14:232–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

