Fluoxetine regulates eEF2 activity (phosphorylation) via HDAC1 inhibitory mechanism in an LPS-induced mouse model of depression
- PMID: 33526073
- PMCID: PMC7852137
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-021-02091-5
Fluoxetine regulates eEF2 activity (phosphorylation) via HDAC1 inhibitory mechanism in an LPS-induced mouse model of depression
Erratum in
-
Correction: Fluoxetine regulates eEF2 activity (phosphorylation) via HDAC1 inhibitory mechanism in an LPS-induced mouse model of depression.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Dec 29;19(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02649-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 36581861 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Selective serotonin reuptaker inhibitors, including fluoxetine, are widely studied and prescribed antidepressants, while their exact molecular and cellular mechanism are yet to be defined. We investigated the involvement of HDAC1 and eEF2 in the antidepressant mechanisms of fluoxetine using a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced depression-like behavior model.
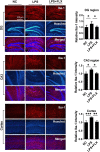
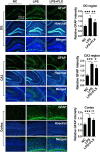
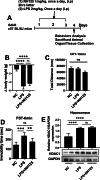
Methods: For in vivo analysis, mice were treated with LPS (2 mg/kg BW), fluoxetine (20 mg/kg BW), HDAC1 activator (Exifone: 54 mg/kg BW) and NH125 (1 mg/kg BW). Depressive-like behaviors were confirmed via behavior tests including OFT, FST, SPT, and TST. Cytokines were measured by ELISA while Iba-1 and GFAP expression were determined by immunofluorescence. Further, the desired gene expression was measured by immunoblotting. For in vitro analysis, BV2 cell lines were cultured; treated with LPS, exifone, and fluoxetine; collected; and analyzed.
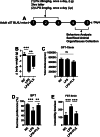
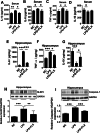
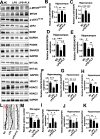
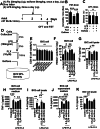
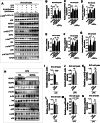
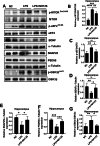
Results: Mice treated with LPS displayed depression-like behaviors, pronounced neuroinflammation, increased HDAC1 expression, and reduced eEF2 activity, as accompanied by altered synaptogenic factors including BDNF, SNAP25, and PSD95. Fluoxetine treatment exhibited antidepressant effects and ameliorated the molecular changes induced by LPS. Exifone, a selective HDAC1 activator, reversed the antidepressant and anti-inflammatory effects of fluoxetine both in vivo and in vitro, supporting a causing role of HDAC1 in neuroinflammation allied depression. Further molecular mechanisms underlying HDAC1 were explored with NH125, an eEF2K inhibitor, whose treatment reduced immobility time, altered pro-inflammatory cytokines, and NLRP3 expression. Moreover, NH125 treatment enhanced eEF2 and GSK3β activities, BDNF, SNAP25, and PSD95 expression, but had no effects on HDAC1.
Conclusions: Our results showed that the antidepressant effects of fluoxetine may involve HDAC1-eEF2 related neuroinflammation and synaptogenesis.
Keywords: Depression; Fluoxetine; HDAC1-eEF2; Neuroinflammation; Synaptogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Liu Q, He H, Yang J, Feng X, Zhao F, Lyu J. Changes in the global burden of depression from 1990 to 2017: findings from the Global Burden of Disease study. Journal of Psychiatric Research. 2020;126:134–140. - PubMed
-
- Driessen E, Dekker JJM, Peen J, Van HL, Maina G, Rosso G, Rigardetto S, Cuniberti F, Vitriol VG, Florenzano RU, et al. The efficacy of adding short-term psychodynamic psychotherapy to antidepressants in the treatment of depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. Clin Psychol Rev. 2020;80:101886. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

