Comparative Efficacy of the Novel Diarylquinoline TBAJ-587 and Bedaquiline against a Resistant Rv0678 Mutant in a Mouse Model of Tuberculosis
- PMID: 33526488
- PMCID: PMC8097419
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02418-20
Comparative Efficacy of the Novel Diarylquinoline TBAJ-587 and Bedaquiline against a Resistant Rv0678 Mutant in a Mouse Model of Tuberculosis
Abstract
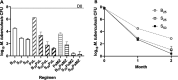
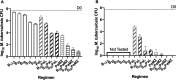
Since its conditional approval in 2012, bedaquiline (BDQ) has been a valuable tool for treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis. More recently, a novel short-course regimen combining BDQ with pretomanid and linezolid won approval to treat highly drug-resistant tuberculosis. Clinical reports of emerging BDQ resistance have identified mutations in Rv0678 that derepress the expression of the MmpL5/MmpS5 efflux transporter as the most common cause. Because the effect of these mutations on bacterial susceptibility to BDQ is relatively small (e.g., 2 to 8× MIC shift), increasing the BDQ dose would increase antibacterial activity but also pose potential safety concerns, including QTc prolongation. Substitution of BDQ with another diarylquinoline with superior potency and/or safety has the potential to overcome these limitations. TBAJ-587 has greater in vitro potency than BDQ, including against Rv0678 mutants, and may offer a larger safety margin. Using a mouse model of tuberculosis and different doses of BDQ and TBAJ-587, we found that against wild-type M. tuberculosis H37Rv and an isogenic Rv0678 mutant, TBAJ-587 has greater efficacy against both strains than BDQ, whether alone or in combination with pretomanid and either linezolid or moxifloxacin and pyrazinamide. TBAJ-587 also reduced the emergence of resistance to diarylquinolines and pretomanid.
Keywords: drug resistance; linezolid; moxifloxacin; pretomanid; pyrazinamide.
Copyright © 2021 Xu et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Efficacy of the Novel Diarylquinoline TBAJ-876 and Bedaquiline against a Resistant Rv0678 Mutant in a Mouse Model of Tuberculosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Nov 17;65(12):e0141221. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01412-21. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 34570644 Free PMC article.
-
Bedquiline Resistance Mutations: Correlations with Drug Exposures and Impact on the Proteome in M. tuberculosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023 Jul 18;67(7):e0153222. doi: 10.1128/aac.01532-22. Epub 2023 May 31. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023. PMID: 37255473 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Generation Diarylquinolines Improve Sterilizing Activity of Regimens with Pretomanid and the Novel Oxazolidinone TBI-223 in a Mouse Tuberculosis Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023 Apr 18;67(4):e0003523. doi: 10.1128/aac.00035-23. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023. PMID: 36920217 Free PMC article.
-
A Narrative Review of Bedaquiline and Delamanid: New Arsenals Against Multidrug-Resistant and Extensively Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2024 Aug;38(15-16):e25091. doi: 10.1002/jcla.25091. J Clin Lab Anal. 2024. PMID: 39431709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of bedaquiline resistance in patients with drug-resistant tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 May 12;25(1):689. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-11067-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40355818 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The pipeline of new molecules and regimens against drug-resistant tuberculosis.J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2021 Nov 5;25:100285. doi: 10.1016/j.jctube.2021.100285. eCollection 2021 Dec. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2021. PMID: 34816020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the cytochrome bc1 complex for drug development in M. tuberculosis: review.Mol Divers. 2022 Oct;26(5):2949-2965. doi: 10.1007/s11030-021-10335-y. Epub 2021 Nov 11. Mol Divers. 2022. PMID: 34762234 Review.
-
Analysis of the Clinical Pipeline of Treatments for Drug-Resistant Bacterial Infections: Despite Progress, More Action Is Needed.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Mar 15;66(3):e0199121. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01991-21. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022. PMID: 35007139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Mycobacterial Drug Resistance in Japan: How to Approach This Problem?Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Dec 24;11(1):19. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11010019. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delamanid or pretomanid? A Solomonic judgement!J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022 Mar 31;77(4):880-902. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkab505. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022. PMID: 35089314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. 2019. WHO consolidated guidelines on drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. - PubMed
-
- Andries K, Verhasselt P, Guillemont J, Göhlmann HW, Neefs JM, Winkler H, Van Gestel J, Timmerman P, Zhu M, Lee E, Williams P, de Chaffoy D, Huitric E, Hoffner S, Cambau E, Truffot-Pernot C, Lounis N, Jarlier V. 2005. A diarylquinoline drug active on the ATP synthase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science 307:223–227. doi:10.1126/science.1106753. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Borisov SE, Dheda K, Enwerem M, Romero Leyet R, D'Ambrosio L, Centis R, Sotgiu G, Tiberi S, Alffenaar JW, Maryandyshev A, Belilovski E, Ganatra S, Skrahina A, Akkerman O, Aleksa A, Amale R, Artsukevich J, Bruchfeld J, Caminero JA, Carpena Martinez I, Codecasa L, Dalcolmo M, Denholm J, Douglas P, Duarte R, Esmail A, Fadul M, Filippov A, Davies Forsman L, Gaga M, Garcia-Fuertes JA, García-García JM, Gualano G, Jonsson J, Kunst H, Lau JS, Lazaro Mastrapa B, Teran Troya JL, Manga S, Manika K, González Montaner P, Mullerpattan J, Oelofse S, Ortelli M, Palmero DJ, Palmieri F, Papalia A, Papavasileiou A, Payen MC, Pontali E, et al. 2017. Effectiveness and safety of bedaquiline-containing regimens in the treatment of MDR- and XDR-TB: a multicentre study. Eur Respir J 49:1700387. doi:10.1183/13993003.00387-2017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Diacon AH, Pym A, Grobusch MP, de los Rios JM, Gotuzzo E, Vasilyeva I, Leimane V, Andries K, Bakare N, De Marez T, Haxaire-Theeuwes M, Lounis N, Meyvisch P, De Paepe E, van Heeswijk RP, Dannemann B. 2014. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis and culture conversion with bedaquiline. N Engl J Med 371:723–732. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1313865. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Guglielmetti L, Jaspard M, Le Dû D, Lachâtre M, Marigot-Outtandy D, Bernard C, Veziris N, Robert J, Yazdanpanah Y, Caumes E, Fréchet-Jachym M. 2017. Long-term outcome and safety of prolonged bedaquiline treatment for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Eur Respir J 49:1601799. doi:10.1183/13993003.01799-2016. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

