Metronidazole-induced reversible cerebellar dysfunction
- PMID: 33526534
- PMCID: PMC7852976
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-239227
Metronidazole-induced reversible cerebellar dysfunction
Abstract
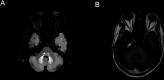
A 73-year-old man who presented with fever and abdominal discomfort was diagnosed to have a liver abscess. He was treated with antimicrobials which included metronidazole. One month into treatment, he developed neurological symptoms and signs that were suggestive of cerebellar pathology. MRI of the brain showed T2/fluid attenuated inversion recovery hyperintensities involving bilateral dentate, fastigial and interpositus nuclei. After excluding common aetiologies, the possibility of metronidazole-induced neurotoxicity was considered. After stopping metronidazole, his symptoms and signs resolved. A subsequent MRI scan of the brain showed reversal of changes. Neurotoxicity caused by metronidazole is an uncommon adverse effect of a commonly used antimicrobial drug and should be considered in the appropriate clinical scenario.
Keywords: drugs: CNS (not psychiatric); neuroimaging; unwanted effects / adverse reactions.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
