Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase in the presence of favipiravir-RTP
- PMID: 33526596
- PMCID: PMC7896311
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2021946118
Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase in the presence of favipiravir-RTP
Abstract
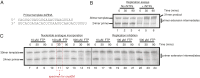
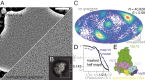
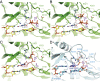
The RNA polymerase inhibitor favipiravir is currently in clinical trials as a treatment for infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), despite limited information about the molecular basis for its activity. Here we report the structure of favipiravir ribonucleoside triphosphate (favipiravir-RTP) in complex with the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) bound to a template:primer RNA duplex, determined by electron cryomicroscopy (cryoEM) to a resolution of 2.5 Å. The structure shows clear evidence for the inhibitor at the catalytic site of the enzyme, and resolves the conformation of key side chains and ions surrounding the binding pocket. Polymerase activity assays indicate that the inhibitor is weakly incorporated into the RNA primer strand, and suppresses RNA replication in the presence of natural nucleotides. The structure reveals an unusual, nonproductive binding mode of favipiravir-RTP at the catalytic site of SARS-CoV-2 RdRp, which explains its low rate of incorporation into the RNA primer strand. Together, these findings inform current and future efforts to develop polymerase inhibitors for SARS coronaviruses.
Keywords: COVID-19; T-705; cryoEM; drug design; structural biology.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chen C., et al. , Favipiravir versus arbidol for COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial. medRxiv [Preprint] (2020). 10.1101/2020.03.17.20037432 (Accessed 1 September 2020). - DOI
-
- Rattanaumpawan P., Jirajariyavej S., Lerdlamyong K., Palavutitotai N., Saiyarin J., Real-world experience with favipiravir for treatment of COVID-19 in Thailand: Results from a multicenter observational study. medRxiv [Preprint] (2020). 10.1101/2020.06.24.20133249 (Accessed 1 September 2020). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

