Peritonsillar Phlegmon: An Addition to the Spectrum of COVID-19
- PMID: 33527050
- PMCID: PMC7842242
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.12369
Peritonsillar Phlegmon: An Addition to the Spectrum of COVID-19
Abstract
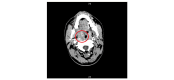
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) epidemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), was first reported in December 2019 in Wuhan, China, then declared to be a pandemic associated with substantial morbidity and mortality. It has shown to exhibit a vast array of symptoms, among which fever, shortness of breath, and cough are the most commonly reported. Lymphadenopathy and tonsillar enlargement is a less common finding reported with this infection. This case describes a patient with tonsillar inflammation which was complicated by peritonsillar phlegmon, with negative throat culture and positive COVID-19 test, suggesting a COVID-19-related etiology of the disease. After the literature search, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case of COVID-related peritonsillar inflammation and phlegmon formation.
Keywords: covid-19; lymphadenopathy; peritonsillar phlegmon; tonsillitis.
Copyright © 2020, Khan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Diagnosis and management of group A streptococcal pharyngitis: a practice guideline. Bisno AL, Gerber MA, Gwaltney JM, Kaplan EL, Schwartz RH. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;25:113–125. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous