Long-term Experience and Outcomes of Programmatic Antiretroviral Therapy for Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 2 Infection in Senegal, West Africa
- PMID: 33527119
- PMCID: PMC7850514
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciaa277
Long-term Experience and Outcomes of Programmatic Antiretroviral Therapy for Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 2 Infection in Senegal, West Africa
Abstract
Background: Programmatic treatment outcome data for people living with human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) in West Africa, where the virus is most prevalent, are scarce.
Methods: Adults with HIV-2 initiating or receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) through the Senegalese national AIDS program were invited to participate in this prospective, longitudinal observational cohort study. We analyzed HIV-2 viral loads, CD4 cell counts, antiretroviral drug resistance, loss to follow-up, and mortality. We also examined changes in treatment guidelines over time and assessed progress toward the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) 90-90-90 targets for HIV-2.
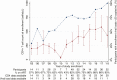
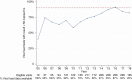
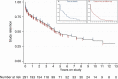
Results: We enrolled 291 participants at 2 sites for 926.0 person-years of follow-up over 13 years. Median follow-up time was 2.2 years per participant. There were 21 deaths reported (7.2%), and 117 individuals (40.2%) were lost to follow-up, including 43 (14.7%) who had an initial visit but never returned for follow-up. CD4 counts and HIV-2 viral suppression (< 50 copies/mL) at enrollment increased over calendar time. Over the study period, 76.7% of plasma viral loads for participants receiving ART were suppressed, and median CD4 gain was 84 cells/μL in participants' first 2 years on study. Since the UNAIDS 90-90-90 strategy was published, 88.1% of viral loads were suppressed. Fifteen percent of patients experienced virologic failure with no known resistance mutations, while 56% had evidence of multiclass drug resistance.
Conclusions: Participants in the Senegalese national AIDS program are initiating ART earlier in the course of disease, and more modern therapeutic regimens have improved outcomes among those receiving therapy. Despite these achievements, HIV-2 treatment remains suboptimal, and significant challenges to improving care remain.
Keywords: 90-90-90; HIV treatment; HIV-2; antiretroviral therapy; viral suppression.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Gottlieb GS, Raugi DN, Smith RA. 90-90-90 for HIV-2? Ending the HIV-2 epidemic by enhancing care and clinical management of patients infected with HIV-2. Lancet HIV 2018; 5:e390–9. - PubMed
-
- Simon F, Matheron S, Tamalet C, et al. Cellular and plasma viral load in patients infected with HIV-2. AIDS 1993; 7:1411–7. - PubMed
-
- Adjorlolo-Johnson G, De Cock KM, Ekpini E, et al. Prospective comparison of mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 and HIV-2 in Abidjan, Ivory Coast. JAMA 1994; 272:462–6. - PubMed
-
- Kanki PJ, Travers KU, MBoup S, et al. Slower heterosexual spread of HIV-2 than HIV-1. Lancet 1994; 343:943–6. - PubMed
-
- Marlink R, Kanki P, Thior I, et al. Reduced rate of disease development after HIV-2 infection as compared to HIV-1. Science 1994; 265:1587–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

