Open-Label, Single-Arm Phase II Study of Pembrolizumab Monotherapy as First-Line Therapy in Patients With Advanced Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 33529051
- PMCID: PMC8078336
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.20.02363
Open-Label, Single-Arm Phase II Study of Pembrolizumab Monotherapy as First-Line Therapy in Patients With Advanced Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Pembrolizumab, a programmed death 1 inhibitor, demonstrated promising single-agent activity in untreated patients with various cancer types. The phase II KEYNOTE-427 study evaluated efficacy and safety of single-agent pembrolizumab in treatment-naive patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC; cohort A) and advanced non-ccRCC (cohort B). Results of cohort A are reported.
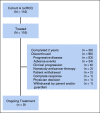
Methods: In this open-label, single-arm phase II study, patients with advanced ccRCC received pembrolizumab 200 mg every 3 weeks for ≤ 24 months. The primary end point was objective response rate by RECIST, version 1.1.
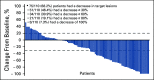
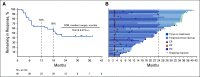
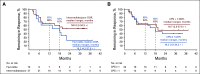
Results: In the total population (N = 110), median time from enrollment to data cutoff was 35.9 (range, 29.5-40.3) months. Objective response rate was 36.4% with four (3.6%) complete responses and 36 (32.7%) partial responses; disease control rate was 58.2% (95% CI, 48.4 to 67.5). Most patients (68.2%) had a decrease in target lesions, including 30.9% with a reduction ≥ 60%. Median duration of response was 18.9 (range, 2.3-37.6+) months; 64.1% of responders had a response ≥ 12 months (Kaplan-Meier). Median progression-free survival was 7.1 months (95% CI, 5.6 to 11.0). Median overall survival was not reached; 12-month and 24-month overall survival rates were 88.2% and 70.8%, respectively. Durable responses were observed across all International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium categories. Grade 3-5 treatment-related adverse events were reported in 30.0% of patients, of which colitis and diarrhea were most frequent.
Conclusion: Single-agent pembrolizumab showed promising antitumor activity as a first-line treatment in patients with advanced ccRCC, with durable responses across International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium categories. Safety and tolerability profile of pembrolizumab monotherapy was comparable to what has been previously described in other tumor types.
Figures

References
-
- Rini BI Plimack ER Stus V, et al. : Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 380:1116-1127, 2019 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

