Cervix Cancer in Sub-Saharan Africa: An Assessment of Cervical Cancer Management
- PMID: 33529076
- PMCID: PMC8081497
- DOI: 10.1200/GO.20.00079
Cervix Cancer in Sub-Saharan Africa: An Assessment of Cervical Cancer Management
Abstract
Purpose: Underdeveloped nations carry the burden of most cervical cancer, yet access to adequate treatment can be challenging. This report assesses the current management of cervical cancer in sub-Saharan Africa to better understand the needs of underdeveloped nations in managing cervical cancer.
Methods: A pre- and postsurvey was sent to all centers participating in the Cervical Cancer Research Network's 4th annual symposium. The pre- and postsurvey evaluated human papillomavirus and HIV screening, resources available for workup and/or treatment, treatment logistics, outcomes, and enrollment on clinical trials. Descriptive analyses were performed on survey responses.
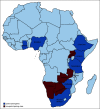
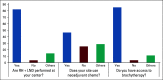
Results: Twenty-nine centers from 12 sub-Saharan countries saw approximately 300 new cases of cervical cancer yearly. Of the countries surveyed, 55% of countries had a human papillomavirus vaccination program and 30% (range, 0%-65%) of women in each region were estimated to have participated in a cervical cancer screening program. In the workup of patients, 43% of centers had the ability to obtain a positron emission tomography and computed tomography scan and 79% had magnetic resonance imaging capabilities. When performing surgery, 88% of those centers had a surgeon with an expertise in performing oncological surgeries. Radiation therapy was available at 96% of the centers surveyed, and chemotherapy was available in 86% of centers. Clinical trials were open at 4% of centers.
Conclusion: There have been significant advancements being made in screening, workup, and management of patients with cervical cancer in sub-Saharan Africa; yet, improvement is still needed. Enrollment in clinical trials remains a struggle. Participants would like to enroll patients on clinical trials with Cervical Cancer Research Network's continuous support.
Conflict of interest statement
Lindsay M. Burt
Memory Bvochora-Nsingo
Rose I. Anorlu
Hannah Simonds
Gita Suneja
David K. Gaffney
Mary McCormak
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization : Cervix uteri fact sheet. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/23-Cervix-uteri-fact-s...
-
- Atun R, Jaffray DA, Barton MB, et al. : Expanding global access to radiotherapy. Lancet Oncol 16:1153-1186, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Peters WA, III, Liu PY, Barrett RJ, II, et al. : Concurrent chemotherapy and pelvic radiation therapy compared with pelvic radiation therapy alone as adjuvant therapy after radical surgery in high-risk early-stage cancer of the cervix. J Clin Oncol 18:1606-1613, 2000 - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization : Human papillomavirus (HPV) and cervical cancer fact sheet. https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/human-papillomavirus...
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

