The role of miR-29 family in disease
- PMID: 33529442
- PMCID: PMC8603934
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.29896
The role of miR-29 family in disease
Abstract
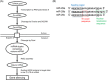
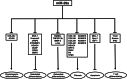
MicroRNAs are small noncoding RNAs that can bind to the target sites in the 3'-untranslated region of messenger RNA to regulate posttranscriptional gene expression. Increasing evidence has identified the miR-29 family, consisting of miR-29a, miR-29b-1, miR-29b-2, and miR-29c, as key regulators of a number of biological processes. Moreover, their abnormal expression contributes to the etiology of numerous diseases. In the current review, we aimed to summarize the differential expression patterns and functional roles of the miR-29 family in the etiology of diseases including osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, cardiorenal, and immune disease. Furthermore, we highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting members of miR-29 family in these diseases. We present miR-29s as promoters of osteoblast differentiation and apoptosis but suppressors of chondrogenic and osteoclast differentiation, fibrosis, and T cell differentiation, with clear avenues for therapeutic manipulation. Further research will be crucial to identify the precise mechanism of miR-29 family in these diseases and their full potential in therapeutics.
Keywords: cardiorenal disease; immune disease; miRNA-29; microRNA; osteoarthritis; osteoporosis.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry Published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

