Cardiac safety of afatinib: a review of data from clinical trials
- PMID: 33530147
- PMCID: PMC7837143
- DOI: 10.1186/s40959-015-0006-7
Cardiac safety of afatinib: a review of data from clinical trials
Abstract
Background: Afatinib is an oral irreversible ErbB family blocker that targets epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR/ErbB1), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2/ErbB2), and HER4 (ErbB4) and is approved for the first-line treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with certain sensitizing EGFR mutations. As anti-HER2 therapies have been associated with cardiac dysfunction, we report cardiac safety data for afatinib.
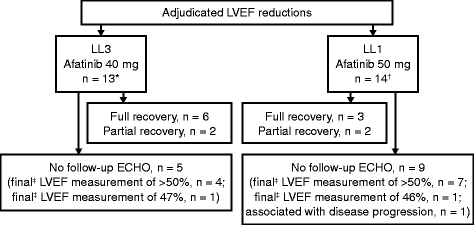
Methods: Cardiac data were analyzed from phase III trials of afatinib 40 mg in treatment-naive patients with EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC (LUX-Lung 3 [LL3]; n = 229 afatinib, n = 111 chemotherapy) and afatinib 50 mg in EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-pretreated NSCLC patients (LUX-Lung 1 [LL1]; n = 390 afatinib, n = 195 placebo). Additional pooled data from 49 trials (n = 3865 afatinib-treated patients) is reported. Cardiac failure adverse events (CF-AEs), including symptomatic cardiac failure and depressed left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), were analyzed.
Results: Time at risk-adjusted CF-AE rates (events/100 patient-years) were similar for afatinib versus placebo in LL1 (2.40 vs 2.23) and versus chemotherapy in LL3 (2.28 vs 2.92); the pooled afatinib CF-AE rate (2.88) was consistent with that for both trials. The frequency of clinically significant LVEF reductions was higher for chemotherapy in LL3 (2/15 [13.3 %], afatinib 13/208 [6.3 %]; p = 0.267) and similar to placebo in LL1 (5/122 [4.1 %], afatinib 14/304 [4.6 %]; p = 1.000).
Conclusion: Afatinib was not associated with cardiac failure or LVEF reductions in the afatinib clinical trial program.
Keywords: Afatinib; Cardiac safety; Non–small cell lung cancer; Tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of dose adjustment on the safety and efficacy of afatinib for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma: post hoc analyses of the randomized LUX-Lung 3 and 6 trials.Ann Oncol. 2016 Nov;27(11):2103-2110. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw322. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27601237 Clinical Trial.
-
[A new perspective in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Role of afatinib: An oral and irreversible ErbB family blocker].Bull Cancer. 2014 Jun;101(6):647-52. doi: 10.1684/bdc.2014.1986. Bull Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24977454 French.
-
Afatinib for the treatment of EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC: A review of clinical findings.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2020 Sep;26(6):1461-1474. doi: 10.1177/1078155220931926. Epub 2020 Jun 20. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2020. PMID: 32567494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Afatinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Uncommon EGFR Mutations Pretreated With Reversible EGFR Inhibitors.Oncologist. 2015 Oct;20(10):1167-74. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0073. Epub 2015 Sep 9. Oncologist. 2015. PMID: 26354527 Free PMC article.
-
Afatinib for the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2014 Apr;15(6):889-903. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2014.902445. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2014. PMID: 24646054 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiovascular disease and lung cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 12;14:1258991. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1258991. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38410099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Major adverse cardiovascular events in advanced-stage lung cancer: a multicenter cohort study.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2024 Jan 18;16:17588359231221907. doi: 10.1177/17588359231221907. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38249337 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular Risks with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Monoclonal Antibody Therapy.Curr Oncol Rep. 2022 Apr;24(4):475-491. doi: 10.1007/s11912-022-01215-1. Epub 2022 Feb 22. Curr Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35192115 Review.
-
Cardiotoxicity of Anticancer Drugs: Molecular Mechanisms and Strategies for Cardioprotection.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 15;9:847012. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.847012. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35497981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Toxicities: Protocols for Monitoring the Adverse Events of Targeted Therapies Used in the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 29;24(11):9429. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119429. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298380 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Solca F, Dahl G, Zoephel A, Bader G, Sanderson M, Klein C, et al. Target binding properties and cellular activity of afatinib (BIBW 2992), an irreversible ErbB family blocker. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012;343:342–50. - PubMed
-
- Ioannou N, Seddon AM, Dalgleish A, Mackintosh D, Modjtahedi H. Treatment with a combination of the ErbB (HER) family blocker afatinib and the IGF-IR inhibitor, NVP-AEW541 induces synergistic growth inhibition of human pancreatic cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:41. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-41. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- GILOTRIF® (afatinib) tablets, for oral use [package insert]. Ridgefield, CT: Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2015.
-
- Sequist LV, Yang JC, Yamamoto N, O'Byrne K, Hirsh V, Mok T, et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3327–34. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
