Changes in Healthy Behaviors and Meeting 24-h Movement Guidelines in Spanish and Brazilian Preschoolers, Children and Adolescents during the COVID-19 Lockdown
- PMID: 33530315
- PMCID: PMC7912043
- DOI: 10.3390/children8020083
Changes in Healthy Behaviors and Meeting 24-h Movement Guidelines in Spanish and Brazilian Preschoolers, Children and Adolescents during the COVID-19 Lockdown
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to assess changes in physical activity, screen time and sleep duration of preschoolers, children and adolescents and the prevalence of meeting the 24-h movement guidelines during the lockdown caused by COVID-19 in a sample from Spain and Brazil.
Methods: A total of 1099 preschoolers, children and adolescents (aged 3-17 years) from Spain (12.1 ± 4.6 years) and Brazil (10.7 ± 4.3 years) were included. An online survey was created and distributed in each country using a snowball sampling strategy. This online survey was completed by parents (mother/father/responsible guardian).
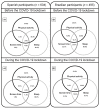
Results: The proportion of the sample who met the PA and ST recommendations decreased during the COVID-19 lockdown in both Spanish and Brazilian samples (p < 0.001), while sleep duration increased (p < 0.001). The proportion of the sample meeting the overall 24-h movement guidelines was very low before the lockdown (Spain 3.0%; Brazil 11.7%) and even worse during the lockdown (Spain 0.3%; Brazil 7.5%).
Conclusions: The prevalence of preschoolers, children and adolescents in both the Spain and Brazil samples meeting the 24-h movement guidelines during COVID-19 restrictions was as low as previous studies in other countries. Efforts to protect and support healthy behaviors of young people during a period of pandemic restrictions need to be a priority.
Keywords: coronavirus; healthy lifestyle; physical activity; sedentary behavior; sleep.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Guidelines on Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviour, and Sleep for Children under 5 Years of Age. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2019. - PubMed
-
- Tremblay M.S., Carson V., Chaput J.-P., Gorber S.C., Dinh T., Duggan M., Faulkner G., Gray C.E., Gruber R., Janson K., et al. Canadian 24-Hour Movement Guidelines for Children and Youth: An Integration of Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviour, and Sleep. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016;41:S311–S327. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2016-0151. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carson V., Hunter S., Kuzik N., Gray C.E., Poitras V.J., Chaput J.-P., Saunders T.J., Katzmarzyk P.T., Okely A.D., Gorber S.C., et al. Systematic Review of Sedentary Behaviour and Health Indicators in School-Aged Children and Youth: An Update. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016;41:S240–S265. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2015-0630. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

