Urinary Single-Cell Profiling Captures the Cellular Diversity of the Kidney
- PMID: 33531352
- PMCID: PMC7920183
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2020050757
Urinary Single-Cell Profiling Captures the Cellular Diversity of the Kidney
Abstract
Background: Microscopic analysis of urine sediment is probably the most commonly used diagnostic procedure in nephrology. The urinary cells, however, have not yet undergone careful unbiased characterization.
Methods: Single-cell transcriptomic analysis was performed on 17 urine samples obtained from five subjects at two different occasions, using both spot and 24-hour urine collection. A pooled urine sample from multiple healthy individuals served as a reference control. In total 23,082 cells were analyzed. Urinary cells were compared with human kidney and human bladder datasets to understand similarities and differences among the observed cell types.
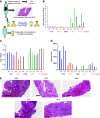
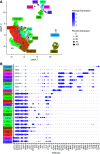
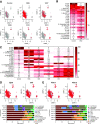
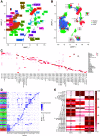
Results: Almost all kidney cell types can be identified in urine, such as podocyte, proximal tubule, loop of Henle, and collecting duct, in addition to macrophages, lymphocytes, and bladder cells. The urinary cell-type composition was subject specific and reasonably stable using different collection methods and over time. Urinary cells clustered with kidney and bladder cells, such as urinary podocytes with kidney podocytes, and principal cells of the kidney and urine, indicating their similarities in gene expression.
Conclusions: A reference dataset for cells in human urine was generated. Single-cell transcriptomics enables detection and quantification of almost all types of cells in the kidney and urinary tract.
Keywords: RNA sequencing; diabetic kidney disease; single-cell transcriptomics; urine.
Copyright © 2021 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Cavanaugh C, Perazella MA: Urine sediment examination in the diagnosis and management of kidney disease: Core curriculum 2019. Am J Kidney Dis 73: 258–272, 2019 - PubMed
-
- Racusen LC, Fivush BA, Andersson H, Gahl WA: Culture of renal tubular cells from the urine of patients with nephropathic cystinosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 1: 1028–1033, 1991 - PubMed
-
- Dörrenhaus A, Müller JI, Golka K, Jedrusik P, Schulze H, Föllmann W: Cultures of exfoliated epithelial cells from different locations of the human urinary tract and the renal tubular system. Arch Toxicol 74: 618–626, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Inoue CN, Sunagawa N, Morimoto T, Ohnuma S, Katsushima F, Nishio T, et al.: Reconstruction of tubular structures in three-dimensional collagen gel culture using proximal tubular epithelial cells voided in human urine. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 39: 364–367, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

