Application of Nanotechnology in the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 33531805
- PMCID: PMC7847377
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S296383
Application of Nanotechnology in the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
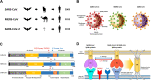
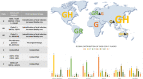
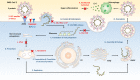
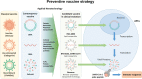
COVID-19, caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection, has been prevalent worldwide for almost a year. In early 2000, there was an outbreak of SARS-CoV, and in early 2010, a similar dissemination of infection by MERS-CoV occurred. However, no clear explanation for the spread of SARS-CoV-2 and a massive increase in the number of infections has yet been proposed. The best solution to overcome this pandemic is the development of suitable and effective vaccines and therapeutics. Fortunately, for SARS-CoV-2, the genome sequence and protein structure have been published in a short period, making research and development for prevention and treatment relatively easy. In addition, intranasal drug delivery has proven to be an effective method of administration for treating viral lung diseases. In recent years, nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems have been applied to intranasal drug delivery to overcome various limitations that occur during mucosal administration, and advances have been made to the stage where effective drug delivery is possible. This review describes the accumulated knowledge of the previous SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV infections and aims to help understand the newly emerged SARS-CoV-2 infection. Furthermore, it elucidates the achievements in developing COVID-19 vaccines and therapeutics to date through existing approaches. Finally, the applicable nanotechnology approach is described in detail, and vaccines and therapeutic drugs developed based on nanomedicine, which are currently undergoing clinical trials, have presented the potential to become innovative alternatives for overcoming COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antiviral drug; nanoparticles; nanotechnology; vaccines.
© 2021 Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that they have no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

