Effect of Micronization on Panax notoginseng: In Vitro Dissolution and In Vivo Bioavailability Evaluations
- PMID: 33531921
- PMCID: PMC7837785
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8831583
Effect of Micronization on Panax notoginseng: In Vitro Dissolution and In Vivo Bioavailability Evaluations
Abstract
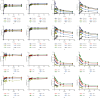
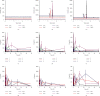
Panax notoginseng (PN) has become the most widely used dietary supplement and herbal in Asian countries. The effect of micronization on PN is not entirely clear. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of particle size of Panax notoginseng powder (PNP) and the potential to improve the bioavailability. The results showed that particle size reduction significantly changed the Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) in vitro dissolution and in vivo pharmacokinetics. The size of the Panax notoginseng powder (PNP) ranges from 60 to 214 μm. The surface morphology and thermal properties of PNP were extensively characterized, and these changes in physicochemical properties of PNP provide a better understanding of the in vitro and in vivo release behaviors of PNS. The in vitro studies demonstrated that the dissolution of PNS and particle size were nonlinear (dose- and size-dependent). The pharmacokinetics parameters of PNP in rats were determined by UHPLC-MS/MS. Powder 4 (90.38 ± 8.28 μm) showed significantly higher AUC0-T values in plasma (P < 0.05). In addition, we also investigated the influence of the hydrothermal treatment of PNP. The results showed that the PNS in vitro release and in vivo bioavailability of PNP pretreatment at 40°C were the highest. This suggests that PNP with a particle size of around 90 μm and heat pretreatment at 40°C would be beneficial. These results provided an experimental basis, and it was beneficial to choose an appropriate particle size and hydrothermal temperature when PNP was used in clinical treatment.
Copyright © 2021 Xiao Liang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of Spray Drying Conditions on Physical Properties of Panax notoginseng Saponin (PNS) Powder and the Intra-Batch Dissolution Variability of PNS Hydrophilic Matrix Tablet.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Mar 30;15:1425-1440. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S295825. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 33833502 Free PMC article.
-
Novel breviscapine nanocrystals modified by panax notoginseng saponins for enhancing bioavailability and synergistic anti-platelet aggregation effect.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019 Mar 1;175:333-342. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.11.067. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019. PMID: 30554011
-
Research on rapid quality identification method of Panax notoginseng powder based on artificial intelligence sensory technology and multi-source information fusion technology.Food Chem. 2024 May 15;440:138210. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.138210. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38118320
-
Anti-diabetic potential of Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS): a review.Phytother Res. 2014 Apr;28(4):510-6. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5026. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Phytother Res. 2014. PMID: 23846979 Review.
-
Panax notoginseng preparation plus aspirin versus aspirin alone on platelet aggregation and coagulation in patients with coronary heart disease or ischemic stroke: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 7;13:1015048. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1015048. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36569332 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

