Salivary gland lesions: diagnostic reliability and challenges of fine needle aspiration cytology
- PMID: 33532023
- PMCID: PMC7847491
Salivary gland lesions: diagnostic reliability and challenges of fine needle aspiration cytology
Abstract
Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a valuable, safe and widely used method for preoperative diagnosis of salivary gland lesions. The diagnostic accuracy of FNAC is dependent on the quality and yield of the aspirate, as well as the experience and knowledge of the cytopathologist. 247 cases of FNAC of salivary gland lesions were performed in our 4-year retrospective study. FNAC diagnoses were divided into non-neoplastic lesions, benign and malignant neoplasms. Histopathologic confirmation was done in 101 cases. The cases with discrepancies between the FNAC and histopathologic results were reviewed to establish possible reasons for discordance. The measures of diagnostic validity of FNAC in diagnosing non-neoplastic, benign and malignant lesions were evaluated. Of the 247 FNAC samples, 135 cases were diagnosed as benign neoplasms, 15 as malignant neoplasms, and 97 as non-neoplastic lesions. Out of the 101 cases with histopathologic confirmation, discordant results between cytologic and histopathologic diagnosis were observed in 15 cases. Our study showed no false positive and 4 false negative results for cancer. Cystic presentation of a lesion was a common reason for diagnostic pitfall. Sensitivity of FNAC in various types of salivary gland lesions ranged from 75%-100%, specificity 81-100%, diagnostic accuracy 85-96%, PPV 31-100% and NPV 60-96%. FNAC is a highly sensitive and specific method for diagnosis of most salivary gland lesions. Despite the fact that histopathology remains the gold standard, preoperative FNAC should be considered for preliminary investigation. Due to the diagnostic pitfalls, FNAC should be used in conjunction with clinical information, physical examination, and radiologic findings to reach the right diagnosis.
Keywords: Salivary gland lesions; cytopathology; diagnostic validity; fine needle aspiration cytology; histopathology.
IJCEP Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



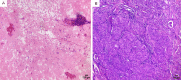
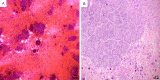
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic accuracy and pitfalls of preoperative fine needle aspiration cytology in salivary gland lesions.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2008 Dec;20(4):358-68. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2008. PMID: 20571594
-
Fine needle aspiration cytology in diagnosis of salivary gland lesions: A study with histologic comparison.Cytojournal. 2013 Jan 31;10:5. doi: 10.4103/1742-6413.109547. Print 2013. Cytojournal. 2013. PMID: 23599724 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) and Permanent Histopathology Results in Salivary Gland Masses.Cureus. 2021 Mar 18;13(3):e13976. doi: 10.7759/cureus.13976. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33884234 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between histopathologic and fine needle aspiration cytology diagnosis of palpable breast lesions: a five-year review.Afr J Med Med Sci. 2007 Dec;36(4):295-8. Afr J Med Med Sci. 2007. PMID: 18564643 Review.
-
Causes of misdiagnoses by thyroid fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC): our experience and a systematic review.Diagn Pathol. 2020 Jan 3;15(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13000-019-0924-z. Diagn Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31900180 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Cautionary Tale: A Case Report Describing a Benign Parotid Oncocytoma Diagnosed as Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma on Fine Needle Aspirate.Cureus. 2023 Dec 20;15(12):e50853. doi: 10.7759/cureus.50853. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38249277 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Lymphoepithelial Carcinoma of the Submandibular Gland: A Case Report.Cureus. 2023 Dec 4;15(12):e49939. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49939. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38179348 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary Gland Ultrasound in Primary Sjögren's Syndrome: Current and Future Perspectives.Open Access Rheumatol. 2022 Sep 1;14:147-160. doi: 10.2147/OARRR.S284763. eCollection 2022. Open Access Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 36072437 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kakoty S, Baruah TD, Babu CPG. FNAC and histopathological correlation of salivary gland lesions: an observational study. Int Surg J. 2017;4:2148–2152.
-
- Parwani AV, Ali SZ. Diagnostic accuracy and pitfalls in fine-needle aspiration interpretation of Warthin tumor. Cancer. 2003;99:166–171. - PubMed
-
- Schindler S, Nayar R, Dutra J, Bedrossian CW. Diagnostic challenges in aspiration cytology of the salivary glands. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2001;18:124–146. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
