Recent advances in drug delivery systems for targeting cancer stem cells
- PMID: 33532180
- PMCID: PMC7838023
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.09.016
Recent advances in drug delivery systems for targeting cancer stem cells
Abstract
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are a subpopulation of cancer cells with functions similar to those of normal stem cells. Although few in number, they are capable of self-renewal, unlimited proliferation, and multi-directional differentiation potential. In addition, CSCs have the ability to escape immune surveillance. Thus, they play an important role in the occurrence and development of tumors, and they are closely related to tumor invasion, metastasis, drug resistance, and recurrence after treatment. Therefore, specific targeting of CSCs may improve the efficiency of cancer therapy. A series of corresponding promising therapeutic strategies based on CSC targeting, such as the targeting of CSC niche, CSC signaling pathways, and CSC mitochondria, are currently under development. Given the rapid progression in this field and nanotechnology, drug delivery systems (DDSs) for CSC targeting are increasingly being developed. In this review, we summarize the advances in CSC-targeted DDSs. Furthermore, we highlight the latest developmental trends through the main line of CSC occurrence and development process; some considerations about the rationale, advantages, and limitations of different DDSs for CSC-targeted therapies were discussed.
Keywords: ABC, ATP binding cassette; AFN, apoferritin; ALDH, aldehyde dehydrogenase; BM-MSCs-derived Exos, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes; Biomarker; CAFs, cancer-associated fibroblasts; CL-siSOX2, cationic lipoplex of SOX2 small interfering RNA; CMP, carbonate-mannose modified PEI; CQ, chloroquine; CSCs, cancer stem cells; Cancer stem cells; Cancer treatment; Cellular level; DCLK1, doublecortin-like kinase 1; DDSs, drug delivery systems; DLE, drug loading efficiency; DOX, doxorubicin; DQA-PEG2000-DSPE, dequlinium and carboxyl polyethylene glycol-distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine; Dex, dexamethasone; Drug delivery systems; ECM, extracellular matrix; EMT, epithelial–mesenchymal transition; EPND, nanodiamond-Epirubicin drug complex; EpCAM, epithelial cell adhesion molecule; GEMP, gemcitabine monophosphate; GLUT1, glucose ligand to the glucose transporter 1; Glu, glucose; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HH, Hedgehog; HIF1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; IONP, iron oxide nanoparticle; LAC, lung adenocarcinoma; LNCs, lipid nanocapsules; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MB, methylene blue; MDR, multidrug resistance; MNP, micellar nanoparticle; MSNs, mesoporous silica nanoparticles; Molecular level; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; Nav, navitoclax; Niche; PBAEs, poly(β-aminoester); PDT, photodynamic therapy; PEG-PCD, poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(2-methyl-2-carboxyl-propylene carbonate-graft-dodecanol); PEG-PLA, poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(d,l-lactide); PEG-b-PLA, poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(d,l-lactide); PLGA, poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide); PTX, paclitaxel; PU-PEI, polyurethane-short branch-polyethylenimine; SLNs, solid lipid nanoparticles; SSCs, somatic stem cells; Sali-ABA, 4-(aminomethyl) benzaldehyde-modified Sali; TNBC, triple negative breast cancer; TPZ, tirapazamine; Targeting strategies; cRGD, cyclic Arg-Gly-Asp; iTEP, immune-tolerant, elastin-like polypeptide; mAbs, monoclonal antibodies; mPEG-b-PCC-g-GEM-g-DC-g-CAT, poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(2-methyl-2-carboxyl-propylenecarbonate-graft-dodecanol-graft-cationic ligands); ncRNA, non-coding RNAs; uPAR, urokinase plasminogen activator receptor.
© 2021 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

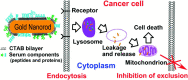
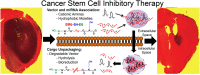

Similar articles
-
Role of integrated cancer nanomedicine in overcoming drug resistance.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013 Nov;65(13-14):1784-802. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2013.07.012. Epub 2013 Jul 21. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013. PMID: 23880506 Review.
-
Small interfering RNA for cancer treatment: overcoming hurdles in delivery.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 Nov;10(11):2075-2109. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.10.005. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 33304780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbon nanotubes for delivery of small molecule drugs.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013 Dec;65(15):1964-2015. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013. PMID: 23954402 Review.
-
Nanoparticles design considerations to co-deliver nucleic acids and anti-cancer drugs for chemoresistance reversal.Int J Pharm X. 2022 Sep 6;4:100126. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2022.100126. eCollection 2022 Dec. Int J Pharm X. 2022. PMID: 36147518 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicle-loaded hydrogels for tissue repair and regeneration.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Dec 21;18:100522. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100522. eCollection 2023 Feb. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 36593913 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunotherapy in liver cancer: overcoming the tolerogenic liver microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 3;15:1460282. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1460282. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39295859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mannose-doped metal-organic frameworks induce tumor cell pyroptosis via the PERK pathway.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Nov 15;21(1):426. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02175-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37968665 Free PMC article.
-
Master Regulators of Causal Networks in Intestinal- and Diffuse-Type Gastric Cancer and the Relation to the RNA Virus Infection Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 13;25(16):8821. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168821. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201509 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria: Insights into Crucial Features to Overcome Cancer Chemoresistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 30;22(9):4770. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094770. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33946271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upregulation of CALD1 predicted a poor prognosis for platinum-treated ovarian cancer and revealed it as a potential therapeutic resistance target.BMC Genomics. 2024 Feb 16;25(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10056-0. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38365611 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . 2019. cancer. [EB/OL] Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer≥.
-
- WHO report on cancer: setting priorities, investing wisely and providing care for all. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2020. https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/igo Available from:
-
- Hidalgo M. Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1605–1617. - PubMed
-
- Reya T., Morrison S.J., Clarke M.F., Weissman I.L. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 2001;414:105–111. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

