Arthroscopic Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Repair With Transtibial Luggage-Tag and Horizontal Mattress Sutures
- PMID: 33532203
- PMCID: PMC7823063
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eats.2020.09.004
Arthroscopic Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Repair With Transtibial Luggage-Tag and Horizontal Mattress Sutures
Abstract
Medial meniscal posterior root repair techniques have shown positive yet varied results in the literature. The decision to perform repair has improved clinical outcomes in many situations, although the healing rate is approximately 64% and the repair strength is roughly one-third of the native root strength, with meniscal extrusion being common. We present a technique based on biomechanical evidence to obtain a strong anatomic posterior root repair to restore nearly normal knee mechanics, combining an increased size of footprint under the lateral aspect of the medial meniscal horn for healing and a luggage-tag suture with a posteriorly placed horizontal mattress suture. The horizontal mattress suture is passed to capture the circumferential fibers of the meniscus and the luggage-tag suture is passed to capture the radial fibers of the meniscal body, through a single transtibial tunnel. The aim of this repair is to restore the normal meniscal function.
© 2020 by the Arthroscopy Association of North America. Published by Elsevier.
Figures
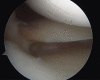
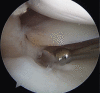
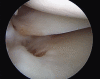
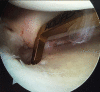

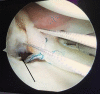
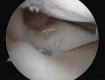

References
-
- Ozkoc G., Circi E., Gonc U., Irgit K., Pourbagher A., Tandogan R.N. Radial tears in the root of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2008;16:849–854. - PubMed
-
- Bin S.I., Kim J.M., Shin S.J. Radial tears of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus. Arthroscopy. 2004;20:373–378. - PubMed
-
- Sonnery-Cottet B., Mortati R., Archbold P., Gadea F., Clechet J., Thaunat M. Root avulsion of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus in skeletally immature patients. Knee. 2014;21:1291–1296. - PubMed
-
- LaPrade C.M., James E.W., Cram T.R., Feagin J.A., Engebretsen L., LaPrade R.F. Meniscal root tears: A classification system based on tear morphology. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43:363–369. - PubMed
-
- Daney B.T., Aman Z.S., Krob J.J. Utilization of transtibial centralization suture best minimizes extrusion and restores tibiofemoral contact mechanics for anatomic medial meniscal root repairs in a cadaveric model. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47:1591–1600. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

