Myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC) key genes analysis in rat anti-CD28-induced immune tolerance kidney transplantation
- PMID: 33532310
- PMCID: PMC7844524
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-20-943
Myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC) key genes analysis in rat anti-CD28-induced immune tolerance kidney transplantation
Abstract
Background: In the field of transplantation, inducing immune tolerance in recipients is of great importance. Blocking co-stimulatory molecule using anti-CD28 antibody could induce tolerance in a rat kidney transplantation model. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) reveals strong immune suppressive abilities in kidney transplantation. Here we analyzed key genes of MDSCs leading to transplant tolerance in this model.
Methods: Microarray data of rat gene expression profiles under accession number GSE28545 in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database were analyzed. Running the LIMMA package in R language, the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were found. Enrichment analysis of the DEGs was conducted in the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) database to explore gene ontology (GO) annotation and their Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways. Their protein-protein interactions (PPIs) were provided by STRING database and was visualized in Cytoscape. Hub genes were carried out by CytoHubba.
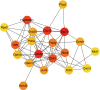
Results: Three hundred and thirty-eight DEGs were exported, including 27 upregulated and 311 downregulated genes. The functions and KEGG pathways of the DEGs were assessed and the PPI network was constructed based on the string interactions of the DEGs. The network was visualized in Cytoscape; the entire PPI network consisted of 192 nodes and 469 edges. Zap70, Cdc42, Stat1, Stat4, Ccl5 and Cxcr3 were among the hub genes.
Conclusions: These key genes, corresponding proteins and their functions may provide valuable background for both basic and clinical research and could be the direction of future studies in immune tolerance, especially those examining immunocyte-induced tolerance.
Keywords: Transplant tolerance; bioinformatics analysis; differentially expressed genes (DEGs); gene ontology (GO); protein-protein network.
2021 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tau-20-943). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics-based screening and analysis of the key genes involved in the influence of antiangiogenesis on myeloid-derived suppressor cells and their effects on the immune microenvironment.Med Oncol. 2024 Mar 25;41(5):96. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02357-x. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38526604
-
Bioinformatic Analysis Combined With Experimental Validation Reveals Novel Hub Genes and Pathways Associated With Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jan 4;8:691966. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.691966. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35059432 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of genes and pathways in esophageal adenocarcinoma using bioinformatics analysis.Biomed Rep. 2018 Oct;9(4):305-312. doi: 10.3892/br.2018.1134. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Biomed Rep. 2018. PMID: 30233782 Free PMC article.
-
Genes associated with inflammation may serve as biomarkers for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease and ischaemic stroke.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Mar 12;19(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01217-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32164735 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the anticancer effects of a novel proteasome inhibitor, ixazomib, on colorectal cancer using a combined method of microarray and bioinformatics analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2017 Jul 19;10:3591-3606. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S139686. eCollection 2017. Onco Targets Ther. 2017. PMID: 28790851 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Uncover diagnostic immunity/hypoxia/ferroptosis/epithelial mesenchymal transformation-related CCR5, CD86, CD8A, ITGAM, and PTPRC in kidney transplantation patients with allograft rejection.Ren Fail. 2022 Dec;44(1):1850-1865. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2141648. Ren Fail. 2022. PMID: 36330810 Free PMC article.
-
Rac and Cdc42 inhibitors reduce macrophage function in breast cancer preclinical models.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 16;13:1152458. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1152458. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37397366 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
