Characteristics of fatty acid composition and minor constituents of red palm olein and palm kernel oil combination
- PMID: 33532350
- PMCID: PMC7832187
- DOI: 10.4103/japtr.JAPTR_91_20
Characteristics of fatty acid composition and minor constituents of red palm olein and palm kernel oil combination
Abstract
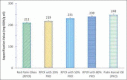
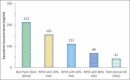
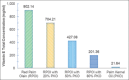
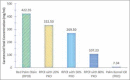
Red palm olein (RPOl) is one of the derivatives of palm oil. It contains a high composition of unsaturated fatty acids such as oleic and linoleic, whereas palm kernel oil (PKO) contains more saturated fatty acids of lauric acid. RPOl provides high nutrient contents such as squalene, Vitamin E, and carotene, whereas PKO that is rich in lauric acid can fight Gram-positive microorganisms. This research aims to study the chemical characteristics of RPOl, PKO, and the combination. A combination of RPOl with four different concentrations of PKO (20%, 50%, 80%, and 100%) was analyzed to obtain the composition of fatty acids, squalene content, Vitamin E levels, total carotene, and saponification numbers. RPOL contains high levels of squalene, Vitamin E, and total carotene, followed by RPOl and PKO combination of oil, with a higher percentage of RPOl in its composition. The increase of the PKO level added to the combination will decrease the saponification number and increasing the acid number. Therefore, it can be concluded that RPOl could be the source of squalene, Vitamin E, carotenoids, and oleic acid, whereas PKO is the largest source of lauric acid.
Keywords: Carotenoids; Vitamin E; fatty acid; palm kernel oil; red palm olein; squalene.
Copyright: © 2021 Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ketaren S. Pengantar Teknologi Minyak Dan Lemak Pangan. 1st ed. Jakarta: Universitas Indonesia Piublishers; 1986. p. 250.
-
- Sinaga AG, Siahaan D, Sinaga KR. Potensi Minyak Sawit Merah Dan Karotenoid Sebagai Suplemen Antioksidan Dalam Pengujian Toleransi Glukosa Pada Tikus Putih (Preliminary Study) Medan, Indonesia. TM Conference Series 01. 2018:251–6.
-
- Ulfah M, Ruswanto A, Ngatirah N. Karakteristik minyak campuran dari red palm oil dengan palm kernel olein. Agritech. 2016;36:145–51.
-
- Gunstone FD. Vegetables Oils In Food Technology: Composition, Properties and Uses. New York: Blackwell Publishing Ltd; 2002. p. 76.
-
- Njoku PC, Egbukole MO, Enenebeaku CK. Physio-chemical characteristics and dietary metal levels of oil from elaeis guineensis species. Pak J Nutr. 2010;9:137–40.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
