S-deoxydihydroglyparvin from Glycosmis parva inhibits lipopolysaccharide induced murine macrophage activation through inactivating p38 mitogen activated protein kinase
- PMID: 33532352
- PMCID: PMC7832183
- DOI: 10.4103/japtr.JAPTR_64_20
S-deoxydihydroglyparvin from Glycosmis parva inhibits lipopolysaccharide induced murine macrophage activation through inactivating p38 mitogen activated protein kinase
Abstract
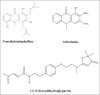
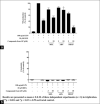
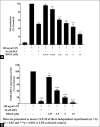
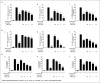
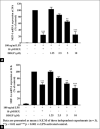
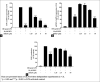
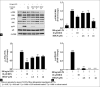
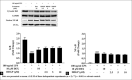
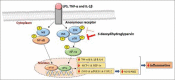
Macrophages play major roles to produce several pro-inflammatory and inflammatory mediators in chronic inflammatory diseases. All current anti-inflammatory drugs target these mediators to alleviate inflammation. Searching for new anti-inflammatory agents is always needed due to problems from the clinical use of current anti-inflammatory drugs. We intended to evaluate the anti-inflammatory potential of three main compounds, arborinine, methylatalaphylline, and S-deoxydihydroglyparvin (DDGP), from Glycosmis parva leaves and branches on macrophage stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Only DDGP demonstrated a potent inhibitor of LPS-activated macrophages. Results indicated that the mRNA level of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) was inhibited by the treatment in accompany with the decreased nitric oxide (IC50 at 3.47 ± 0.1 μM). DDGP was shown to suppress tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1, and IL-6 at the mRNA expression and at the released protein levels. In addition, DDGP inhibited the several chemokines, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and macrophage inflammatory proteins-1α, and enzymes for prostaglandin (PG) synthesis. It also inhibited PGE2 production. On LPS signaling pathways, DDGP profoundly decreased phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in the LPS-treated cells. It had little or no effect on the activation of JNK, ERK and nuclear factor kappa B. In conclusion, results suggested that DDGP from G. parva inhibited expression and production of inflammatory molecules in LPS-activated macrophages through suppressing p38 MAPK activation. DDGP should be a good candidate anti-inflammatory agent in the future.
Keywords: Anti-inflammation; Glycosmis parva; S-deoxydihydroglyparvin; lipopolysaccharide; macrophage.
Copyright: © 2021 Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Xanthii fructus inhibits inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages through suppressing NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 24;176:394-401. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.11.020. Epub 2015 Nov 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26560439
-
A supercritical CO₂ extract from seabuckthorn leaves inhibits pro-inflammatory mediators via inhibition of mitogen activated protein kinase p38 and transcription factor nuclear factor-κB.Int Immunopharmacol. 2012 Aug;13(4):461-7. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2012.05.011. Epub 2012 Jun 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22664145
-
The p38 MAPK inhibitor JLU1124 inhibits the inflammatory response induced by lipopolysaccharide through the MAPK-NF-κB pathway in RAW264.7 macrophages.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Nov;17(3):785-92. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Sep 23. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24070708
-
Cnidilide, an alkylphthalide isolated from the roots of Cnidium officinale, suppresses LPS-induced NO, PGE2, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α production by AP-1 and NF-κB inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Nov;40:146-155. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.08.021. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27591413
-
Myrsine seguinii ethanolic extract and its active component quercetin inhibit macrophage activation and peritonitis induced by LPS by targeting to Syk/Src/IRAK-1.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Feb 12;151(3):1165-1174. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.12.033. Epub 2013 Dec 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24378351
Cited by
-
In vitro and in silico studies of 7'',8''-buddlenol D anti-inflammatory lignans from Carallia brachiata as p38 MAP kinase inhibitors.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 2;13(1):3558. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30475-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36864126 Free PMC article.
-
Ruta angustifolia Pers. (Narrow-Leaved Fringed Rue): Pharmacological Properties and Phytochemical Profile.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 13;12(4):827. doi: 10.3390/plants12040827. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36840175 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tasneem S, Liu B, Li B, Choudhary MI, Wang W. Molecular pharmacology of inflammation: Medicinal plants as anti-inflammatory agents. Pharmacol Res. 2019;139:126–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
