Improved autosomal STR typing of degraded femur samples extracted using a custom demineralization buffer and DNA IQ™
- PMID: 33532721
- PMCID: PMC7829153
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fsisyn.2020.100131
Improved autosomal STR typing of degraded femur samples extracted using a custom demineralization buffer and DNA IQ™
Abstract
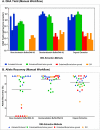
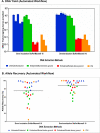
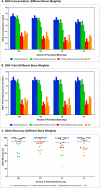
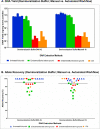
Bone samples are utilized as a source of DNA in disaster victim identification and human remains investigations. However, DNA recovery from bones is time consuming and prone to contamination. A logical approach for postmortem identification is to validate efficient DNA extraction methods requiring less bone material using improved molecular kits with less hands-on time and workflows that facilitate faster turn-around time for processing. In this study, we evaluated DNA yield and amplification efficiency of DNA extracts using a new custom bone demineralization buffer (DMB; Promega) and extracted via manual and automated DNA IQ™ workflows. Including the demineralization step, the bone protocol can be completed in ∼4 h and even less with minimal sample handling when automated. Overall, a rapid and simple DNA extraction with improved allele recovery was validated using degraded bone samples exposed to tropical environments and post-disaster recovery as well as adverse conditions of embalming prior to internment.
Keywords: Automation; Autosomal STR; Bone; DNA extraction; Demineralization; Forensic.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Ward J. Best practice recommendations for the establishment of a national DNA identification program for missing persons: a global perspective. Forensic Sci. Int.: Genetics Supplement Series. 2017;6:e43–e45.
-
- Watherston J., McNevin D., Gahan M.E., Bruce D., Ward J. Current and emerging tools for the recovery of genetic information from postmortem samples: new directions for disaster victim identification. Forensic Sci. Int.: Genetics. 2018;37:270–282. - PubMed
-
- Edson S.M., McMahon T.P. Extraction of DNA from skeletal remains. In: Goodwin W., editor. Forensic DNA Typing Protocols. Humana Press; New York, NY: 2016. pp. 69–87.
-
- Loreille O.M., Diegoli T.M., Irwin J.A., Coble M.D., Parsons T.J. High efficiency DNA extraction from bone by total demineralization. Forensic Sci. Int.: Genetics. 2007;1(2):191–195. - PubMed
-
- Lee H.Y., Park M.J., Kim N.Y., Sim J.E., Yang W.I., Shin K.J. Simple and highly effective DNA extraction methods from old skeletal remains using silica columns. Forensic Sci. Int.: Genetics. 2010;4(5):275–280. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

