Metabolic engineering of Pseudomonas putida for production of vanillylamine from lignin-derived substrates
- PMID: 33533574
- PMCID: PMC8601178
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.13764
Metabolic engineering of Pseudomonas putida for production of vanillylamine from lignin-derived substrates
Abstract
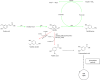
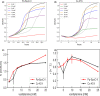
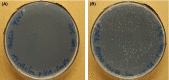
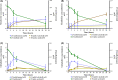
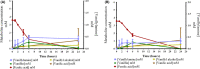
Whole-cell bioconversion of technical lignins using Pseudomonas putida strains overexpressing amine transaminases (ATAs) has the potential to become an eco-efficient route to produce phenolic amines. Here, a novel cell growth-based screening method to evaluate the in vivo activity of recombinant ATAs towards vanillylamine in P. putida KT2440 was developed. It allowed the identification of the native enzyme Pp-SpuC-II and ATA from Chromobacterium violaceum (Cv-ATA) as highly active towards vanillylamine in vivo. Overexpression of Pp-SpuC-II and Cv-ATA in the strain GN442ΔPP_2426, previously engineered for reduced vanillin assimilation, resulted in 94- and 92-fold increased specific transaminase activity, respectively. Whole-cell bioconversion of vanillin yielded 0.70 ± 0.20 mM and 0.92 ± 0.30 mM vanillylamine, for Pp-SpuC-II and Cv-ATA, respectively. Still, amine production was limited by a substantial re-assimilation of the product and formation of the by-products vanillic acid and vanillyl alcohol. Concomitant overexpression of Cv-ATA and alanine dehydrogenase from Bacillus subtilis increased the production of vanillylamine with ammonium as the only nitrogen source and a reduction in the amount of amine product re-assimilation. Identification and deletion of additional native genes encoding oxidoreductases acting on vanillin are crucial engineering targets for further improvement.
© 2021 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by Society for Applied Microbiology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdelaziz, O.Y. , Brink, D.P. , Prothmann, J. , Ravi, K. , Sun, M. , García‐Hidalgo, J. , et al. (2016) Biological valorization of low molecular weight lignin. Biotechnol Adv 34: 1318–1346. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, M. , Afewerki, S. , Berglund, P. , and Cõrdova, A. (2014) Total synthesis of capsaicin analogues from lignin‐derived compounds by combined heterogeneous metal, organocatalytic and enzymatic cascades in one pot. Adv Synth Catal 356: 2113–2118.
-
- Arce‐Rodríguez, M.L. , and Ochoa‐Alejo, N. (2019) Biochemistry and molecular biology of capsaicinoid biosynthesis: recent advances and perspectives. Plant Cell Rep 38: 1017–1030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

