Paeonol attenuates inflammation by confining HMGB1 to the nucleus
- PMID: 33534963
- PMCID: PMC7957162
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16319
Paeonol attenuates inflammation by confining HMGB1 to the nucleus
Abstract
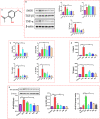
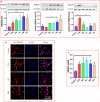
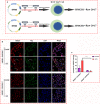
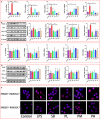
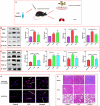
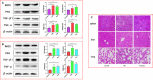
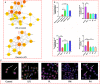
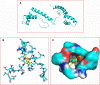
Inflammation is a biological process that exists in a large number of diseases. If the magnitude or duration of inflammation becomes uncontrolled, inflammation may cause pathological damage to the host. HMGB1 and NF-κB have been shown to play pivotal roles in inflammation-related diseases. New drugs aimed at inhibiting HMGB1 expression have become a key research focus. In the present study, we showed that paeonol (Pae), the main active component of Paeonia suffruticosa, decreases the expression of inflammatory cytokines and inhibits the translocation of HMGB1 induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). By constructing HMGB1-overexpressing (HMGB1+ ) and HMGB1-mutant (HMGB1m ) RAW264.7 cells, we found that the nuclear HMGB1 could induce an LPS-tolerant state in RAW264.7 cells and that paeonol had no influence on the expression of inflammatory cytokines in HMGB1m RAW264.7 cells. In addition, the anti-inflammatory property of paeonol was lost in HMGB1 conditional knockout mice, indicating that HMGB1 is a target of paeonol and a mediator through which paeonol exerts its anti-inflammatory function. Additionally, we also found that HMGB1 and P50 competitively bound with P65, thus inactivating the NF-κB pathway. Our research confirmed the anti-inflammation property of paeonol and suggests that inhibiting the translocation of HMGB1 could be a new strategy for treating inflammation.
Keywords: HMGB1; NF-κB; P65; inflammation; paeonol.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature. 2017;542:177‐185. - PubMed
-
- Galvão I, Michelle A. Mediators of inflammation. Immunopharmacol. Inflamm. 2018;21:112‐118.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

