The Role of the Renal Dopaminergic System and Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Hypertension
- PMID: 33535566
- PMCID: PMC7912729
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9020139
The Role of the Renal Dopaminergic System and Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Hypertension
Abstract
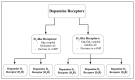
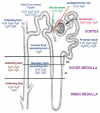
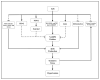
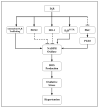
The kidney is critical in the long-term regulation of blood pressure. Oxidative stress is one of the many factors that is accountable for the development of hypertension. The five dopamine receptor subtypes (D1R-D5R) have important roles in the regulation of blood pressure through several mechanisms, such as inhibition of oxidative stress. Dopamine receptors, including those expressed in the kidney, reduce oxidative stress by inhibiting the expression or action of receptors that increase oxidative stress. In addition, dopamine receptors stimulate the expression or action of receptors that decrease oxidative stress. This article examines the importance and relationship between the renal dopaminergic system and oxidative stress in the regulation of renal sodium handling and blood pressure. It discusses the current information on renal dopamine receptor-mediated antioxidative network, which includes the production of reactive oxygen species and abnormalities of renal dopamine receptors. Recognizing the mechanisms by which renal dopamine receptors regulate oxidative stress and their degree of influence on the pathogenesis of hypertension would further advance the understanding of the pathophysiology of hypertension.
Keywords: blood pressure; dopamine; dopamine receptor; dopaminergic system; hypertension; kidney; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflict of interest related to the findings on this topic.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Renal Dopamine Receptors and Oxidative Stress: Role in Hypertension.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021 Mar 20;34(9):716-735. doi: 10.1089/ars.2020.8106. Epub 2020 May 29. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021. PMID: 32349533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of renal dopamine D1 receptor function during oxidative stress.Hypertension. 2015 May;65(5):1064-72. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05255. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Hypertension. 2015. PMID: 25733244 Free PMC article.
-
Renal dopamine receptors, oxidative stress, and hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Aug 27;14(9):17553-72. doi: 10.3390/ijms140917553. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23985827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress causes renal dopamine D1 receptor dysfunction and salt-sensitive hypertension in Sprague-Dawley rats.Hypertension. 2008 Feb;51(2):367-75. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.102111. Epub 2007 Dec 24. Hypertension. 2008. PMID: 18158345
-
Upregulation of renal D5 dopamine receptor ameliorates the hypertension in D3 dopamine receptor-deficient mice.Hypertension. 2013 Aug;62(2):295-301. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.01483. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Hypertension. 2013. PMID: 23753418 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mediating effect of oxidative stress on blood pressure elevation in workers exposed to low concentrations of benzene, toluene, and xylene (BTX).Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 30;14(1):26139. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77689-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39478173 Free PMC article.
-
The dopaminergic system mediates the lateral habenula-induced autonomic cardiovascular responses.Front Physiol. 2024 Nov 21;15:1496726. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1496726. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39640253 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for a relationship between genetic polymorphisms of the L-DOPA transporter LAT2/4F2hc and risk of hypertension in the context of chronic kidney disease.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Jun 18;17(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-01935-2. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38890684 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxiredoxin-4 and Dopamine D5 Receptor Interact to Reduce Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in the Kidney.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 Jun;38(16-18):1150-1166. doi: 10.1089/ars.2022.0034. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 36401517 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of rutin supplement on blood pressure markers, some serum antioxidant enzymes, and quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus compared with placebo.Front Nutr. 2023 Aug 3;10:1214420. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1214420. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37599700 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

