USH2A-Related Retinitis Pigmentosa: Staging of Disease Severity and Morpho-Functional Studies
- PMID: 33535592
- PMCID: PMC7912870
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11020213
USH2A-Related Retinitis Pigmentosa: Staging of Disease Severity and Morpho-Functional Studies
Abstract
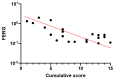
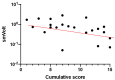
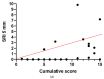
Usher syndrome type 2A (USH2A) is a genetic disease characterized by bilateral neuro-sensory hypoacusia and retinitis pigmentosa (RP). While several methods, including electroretinogram (ERG), describe retinal function in USH2A patients, structural alterations can be assessed by optical coherence tomography (OCT). According to a recent collaborative study, RP can be staged considering visual acuity, visual field area and ellipsoid zone (EZ) width. The aim of this study was to retrospectively determine RP stage in a cohort of patients with USH2A gene variants and to correlate the results with age, as well as additional functional and morphological parameters. In 26 patients with established USH2A genotype, RP was staged according to recent international standards. The cumulative staging score was correlated with patients' age, amplitude of full-field and focal flicker ERGs, and the OCT-measured area of sub-Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) illumination (SRI). RP cumulative score (CS) was positively correlated (r = 0.6) with age. CS was also negatively correlated (rho = -0.7) with log10 ERG amplitudes and positively correlated (r = 0.5) with SRI. In USH2A patients, RP severity score is correlated with age and additional morpho-functional parameters not included in the international staging system and can reliably predict their abnormality at different stages of disease.
Keywords: Usher 2A gene; Usher syndrome; electroretinogram; retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) and outer retina atrophy (RORA); retinitis pigmentosa; staging; sub-RPE illumination (SRI).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

