Immune Actions on the Peripheral Nervous System in Pain
- PMID: 33535595
- PMCID: PMC7867183
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22031448
Immune Actions on the Peripheral Nervous System in Pain
Abstract
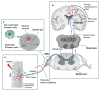
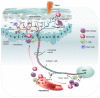
Pain can be induced by tissue injuries, diseases and infections. The interactions between the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and immune system are primary actions in pain sensitizations. In response to stimuli, nociceptors release various mediators from their terminals that potently activate and recruit immune cells, whereas infiltrated immune cells further promote sensitization of nociceptors and the transition from acute to chronic pain by producing cytokines, chemokines, lipid mediators and growth factors. Immune cells not only play roles in pain production but also contribute to PNS repair and pain resolution by secreting anti-inflammatory or analgesic effectors. Here, we discuss the distinct roles of four major types of immune cells (monocyte/macrophage, neutrophil, mast cell, and T cell) acting on the PNS during pain process. Integration of this current knowledge will enhance our understanding of cellular changes and molecular mechanisms underlying pain pathogenies, providing insights for developing new therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: immune response; inflammation; pain; peripheral nervous system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

