Family Function, Quality of Life, and Well-Being in Parents of Infants With Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
- PMID: 33535863
- PMCID: PMC8594631
- DOI: 10.1177/1074840720987309
Family Function, Quality of Life, and Well-Being in Parents of Infants With Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
Abstract
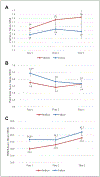
Survival for hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) has improved dramatically. Little is known about early family function, quality of life (QOL), or well-being/adjustment for parents of infants with HLHS. Parent/family outcomes over time, predictors, and differences in 143 mothers and 72 fathers were examined. Parents reported better family function compared with published norms, but 26% experienced family dysfunction. QOL and well-being were significantly lower than adult norms. QOL scores generally declined over time, whereas self-reported well-being improved. Responses from mothers and fathers showed different trends, with mothers having worse scores on most measures and at most time points. Being a single parent was a risk factor for poorer family function, but not for lower individual QOL or well-being. Family characteristics, stress, and coping skills were predictive of outcomes. Parents' psychosocial responses to the challenges of life with infants with HLHS change over time. Individually tailored psychosocial support is needed.
Keywords: congenital heart disease; family; quality of life; well-being.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

