AGLR is a novel index for the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a retrospective study
- PMID: 33536005
- PMCID: PMC7860009
- DOI: 10.1186/s12893-020-01037-7
AGLR is a novel index for the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Most hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients' liver function indexes are abnormal. We aimed to investigate the relationship between (alkaline phosphatase + gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase)/lymphocyte ratio (AGLR) and the progression as well as the prognosis of HCC.
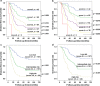
Methods: A total of 495 HCC patients undergoing radical hepatectomy were retrospectively analyzed. We randomly divided these patients into the training cohort (n = 248) and the validation cohort (n = 247). In the training cohort, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to determine the optimal cut-off value of AGLR for predicting postoperative survival of HCC patients, and the predictive value of AGLR was evaluated by concordance index (C-index). Further analysis of clinical and biochemical data of patients and the correlation analysis between AGLR and other clinicopathological factors were finished. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to identify prognostic factors for HCC patients. Survival curves were analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method.
Results: According to the ROC curve analysis, the optimal predictive cut-off value of AGLR was 90. The C-index of AGLR was 0.637 in the training cohort and 0.654 in the validation cohort, respectively. Based on this value, the HCC patients were divided into the low-AGLR group (AGLR ≤ 90) and the high-AGLR group (AGLR > 90). Preoperative AGLR level was positively correlated with alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), tumor size, tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage, and microvascular invasion (MVI) (all p < 0.05). In the training and validation cohorts, patients with AGLR > 90 had significantly shorter OS than patients with AGLR ≤ 90 (p < 0.001). Univariate and multivariate analyses of the training cohort (HR, 1.79; 95% CI 1.21-2.69; p < 0.001) and validation cohort (HR, 1.82; 95% CI 1.35-2.57; p < 0.001) had identified AGLR as an independent prognostic factor. A new prognostic scoring model was established based on the independent predictors determined in multivariate analysis.
Conclusions: The elevated preoperative AGLR level indicated poor prognosis for patients with HCC; the novel prognostic scoring model had favorable predictive capability for postoperative prognosis of HCC patients, which may bring convenience for clinical management.
Keywords: AGLR; Biomarker; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Predictive value of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase to lymphocyte count ratio in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with microvascular invasion.BMC Cancer. 2020 Feb 18;20(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-6628-7. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32070301 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive nomograms based on gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase to prealbumin ratio for prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients without microvascular invasion.BMC Cancer. 2024 May 21;24(1):617. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12387-3. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38773511 Free PMC article.
-
[A new prognostic score system of hepatocellular carcinoma following hepatectomy].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2017 Dec 23;39(12):903-909. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2017.12.005. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29262506 Chinese.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of Gamma-Glutamyltransferase in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 May;98(19):e15603. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015603. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31083251 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts the risk of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Int J Biol Markers. 2019 Sep;34(3):213-220. doi: 10.1177/1724600819874487. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Int J Biol Markers. 2019. PMID: 31507240 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma from Embryogenic Antigens to cfDNA.Biomedicines. 2025 Apr 23;13(5):1020. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051020. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40426850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel index for the prediction of significant liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis B patients in China.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Jul 21;28(27):3503-3513. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i27.3503. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36158257 Free PMC article.
-
Linoleic acid pathway disturbance contributing to potential cancerization of intrahepatic bile duct stones into intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 May 30;22(1):269. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02354-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35637430 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights Into a Classification-Based Microvascular Invasion Prediction Model in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter Study.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 31;12:796311. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.796311. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35433417 Free PMC article.
-
Reappraisal of the Role of Alkaline Phosphatase in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Pers Med. 2022 Mar 23;12(4):518. doi: 10.3390/jpm12040518. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35455635 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

