Identification of 38 novel loci for systemic lupus erythematosus and genetic heterogeneity between ancestral groups
- PMID: 33536424
- PMCID: PMC7858632
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21049-y
Identification of 38 novel loci for systemic lupus erythematosus and genetic heterogeneity between ancestral groups
Abstract
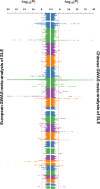
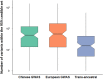
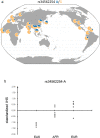
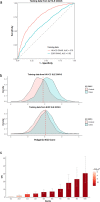
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a worldwide autoimmune disease with high heritability, shows differences in prevalence, severity and age of onset among different ancestral groups. Previous genetic studies have focused more on European populations, which appear to be the least affected. Consequently, the genetic variations that underlie the commonalities, differences and treatment options in SLE among ancestral groups have not been well elucidated. To address this, we undertake a genome-wide association study, increasing the sample size of Chinese populations to the level of existing European studies. Thirty-eight novel SLE-associated loci and incomplete sharing of genetic architecture are identified. In addition to the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) region, nine disease loci show clear ancestral differences and implicate antibody production as a potential mechanism for differences in disease manifestation. Polygenic risk scores perform significantly better when trained on ancestry-matched data sets. These analyses help to reveal the genetic basis for disparities in SLE among ancestral groups.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Lawrence JS, Martins CL, Drake GL. A family survey of lupus-erythematosus .1. heritability. J. Rheumatol. 1987;14:913–921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

