A single-dose mRNA vaccine provides a long-term protection for hACE2 transgenic mice from SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33536425
- PMCID: PMC7858593
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21037-2
A single-dose mRNA vaccine provides a long-term protection for hACE2 transgenic mice from SARS-CoV-2
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: A single-dose mRNA vaccine provides a long-term protection for hACE2 transgenic mice from SARS-CoV-2.Nat Commun. 2021 Apr 15;12(1):2355. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22820-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33859203 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
The rapid expansion of the COVID-19 pandemic has made the development of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine a global health and economic priority. Taking advantage of versatility and rapid development, three SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine candidates have entered clinical trials with a two-dose immunization regimen. However, the waning antibody response in convalescent patients after SARS-CoV-2 infection and the emergence of human re-infection have raised widespread concerns about a possible short duration of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine protection. Here, we developed a nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccine in lipid-encapsulated form that encoded the SARS-CoV-2 RBD, termed as mRNA-RBD. A single immunization of mRNA-RBD elicited both robust neutralizing antibody and cellular responses, and conferred a near-complete protection against wild SARS-CoV-2 infection in the lungs of hACE2 transgenic mice. Noticeably, the high levels of neutralizing antibodies in BALB/c mice induced by mRNA-RBD vaccination were maintained for at least 6.5 months and conferred a long-term notable protection for hACE2 transgenic mice against SARS-CoV-2 infection in a sera transfer study. These data demonstrated that a single dose of mRNA-RBD provided long-term protection against SARS-CoV-2 challenge.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
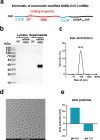
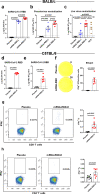
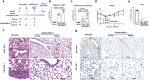
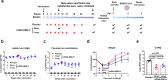
References
-
- Bao, L. et al. The pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 in hACE2 transgenic mice. Nature583, 830–833 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

